MCF51QE128 MCU Series Reference Manual, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 91
Get the latest version from freescale.com
Chapter 4 Memory
One period of the resulting clock (1/f
FCLK
) is used by the command processor to time program and erase
pulses. An integer number of these timing pulses are used by the command processor to complete a
program or erase command.
Program and erase times are given in the MCF51QE128 Data Sheet, order number MCF51QE128DS.
4.6 Security
The MCF51QE128/64/32 includes circuitry to prevent unauthorized access to the contents of flash and
RAM memory. When security is engaged, BDM access is restricted to the upper byte of the debug XCSR,
CSR2, and CSR3 registers. RAM, flash memory, peripheral registers, and most of the CPU register set are
not available via BDM. Programs executing from internal memory have normal access to all MCU
memory locations and resources.
Security is engaged or disengaged based on the state of two nonvolatile register bits (SEC01, SEC00) in
the FOPT register. During reset, the contents of the nonvolatile location, NVOPT, are copied from flash
into the working FOPT register in high-page register space. Engage security by programming the NVOPT
location. This can be done at the same time the flash memory is programmed. The 1:1 state disengages
security and the other three combinations engage security. Security is implemented differently than on the
pin-compatible MC9S08QE128/64/32 family of devices. This is a result of differences inherent in the S08
and ColdFire MCU architectures.
Upon exiting reset, the XCSR[SEC] bit in the ColdFire CPU is set if the device is secured, cleared
otherwise.
You can allow or disallow a security unlocking mechanism through an 8-byte backdoor security key. The
security key can be written by the CPU executing from internal memory. It cannot be entered without the
cooperation of a secure user program. The procedure for this is detailed in Section 4.5.5.1, “Unsecuring
the MCU using Backdoor Key Access”.
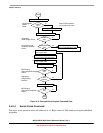
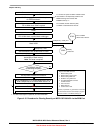
Development tools unsecure devices via an alternate BDM-based methodology shown in Figure 4-15.
Because RESET and BKGD pins can be reprogrammed via software, a power-on-reset is required to be
absolutely certain of obtaining control of the device via BDM, which is a required prerequisite for clearing
security. Other methods (outlined in red in Figure 4-15) can also be used, but may not work under all
circumstances.