Chapter 18 Version 1 ColdFire Debug (CF1_DEBUG)
MCF51QE128 MCU Series Reference Manual, Rev. 3
408 Freescale Semiconductor
Get the latest version from freescale.com
Figure 18-21. ACK Abort Procedure at the Command Level
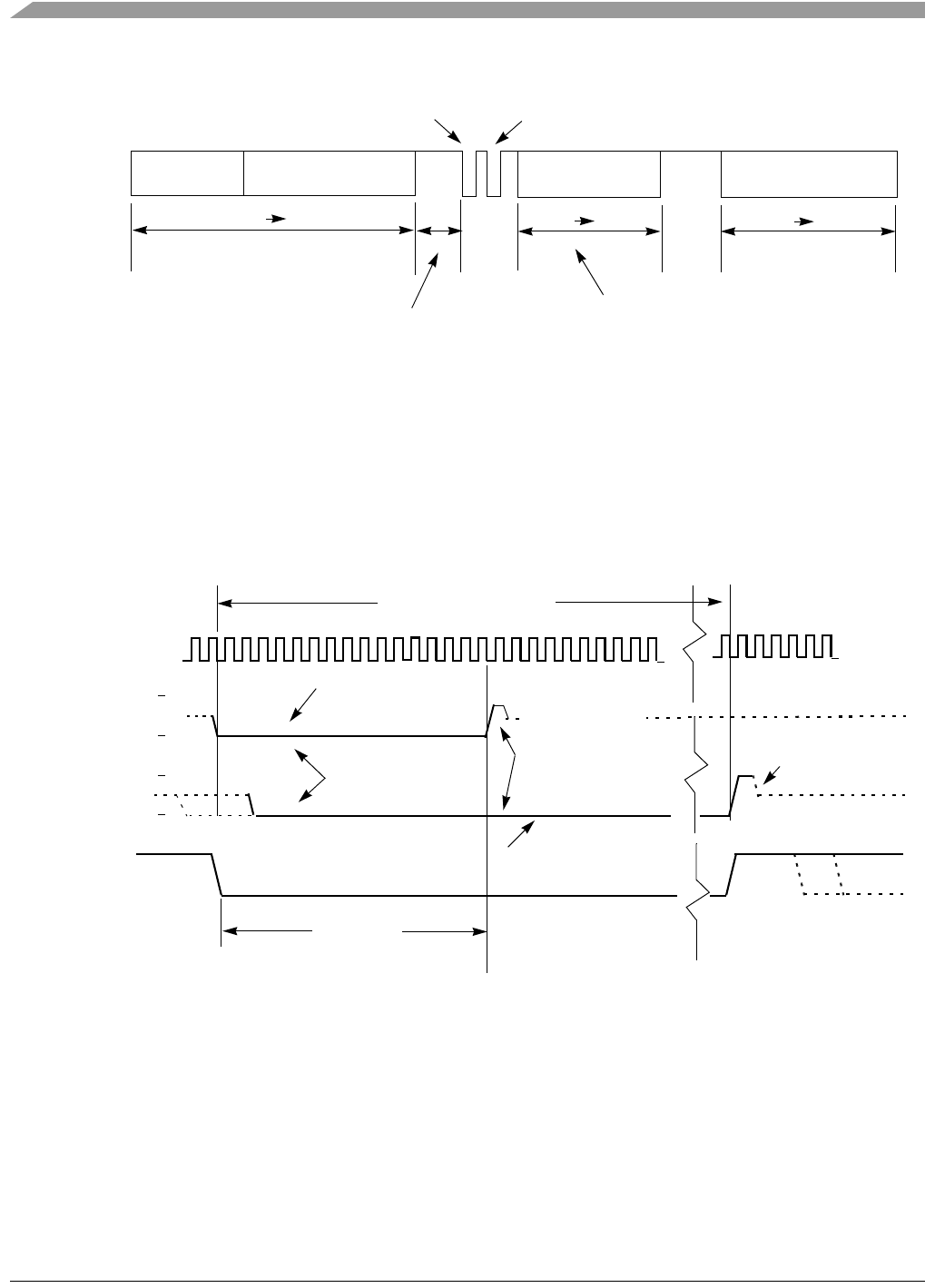
Figure 18-22 a shows a conflict between the ACK pulse and the sync request pulse. This conflict could
occur if a pod device is connected to the target BKGD pin and the target is already executing a BDC
command. Consider that the target CPU is executing a pending BDC command at the exact moment the
pod is being connected to the BKGD pin. In this case, an ACK pulse is issued at the same time as the SYNC
command. In this case there is an electrical conflict between the ACK speedup pulse and the sync pulse.
Since this is not a probable situation, the protocol does not prevent this conflict from happening.
Figure 18-22. ACK Pulse and SYNC Request Conflict
The hardware handshake protocol is enabled by the ACK_ENABLE command and disabled by the
ACK_DISABLE command. It also allows for pod devices to choose between the hardware handshake
protocol or the software protocol that monitors the XCSR status byte. The ACK_ENABLE and
ACK_DISABLE commands are:
• ACK_ENABLE — Enables the hardware handshake protocol. The target issues the ACK pulse
when a CPU command is executed. The ACK_ENABLE command itself also has the ACK pulse
as a response.
READ_MEM.B
READ_XCSR_BYTE
BKGD PIN
ADDRESS[23-0]
HOST TARGET
BDC DECODES
READ_MEM.B CMD
IS ABORTED BY THE SYNC REQUEST
NEW BDC COMMAND
AND CPU TRYS TO EXECUTE
THE READ_MEM.B CMD
HOST TARGET
HOST TARGET
SYNC RESPONSE
FROM THE TARGET
NEW BDC COMMAND
(NOT TO SCALE)
(NOT TO SCALE)
BDC CLOCK
(TARGET MCU)
TARGET MCU
DRIVES TO
BKGD PIN
BKGD PIN
16 CYCLES
SPEEDUP PULSE
HIGH-IMPEDANCE
HOST
DRIVES SYNC
TO BKGD PIN
HOST AND TARGET
ACK PULSE
HOST SYNC REQUEST PULSE
AT LEAST 128 CYCLES
ELECTRICAL CONFLICT
DRIVE TO BKGD PIN


















