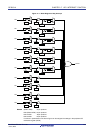
RL78/G1A CHAPTER 17 KEY INTERRUPT FUNCTION
17.4 Key Interrupt Operation
17.4.1 When not using the key interrupt flag (KRMD = 0)
A key interrupt (INTKR) is generated when the valid edge specified by the setting of the KREG bit is input to a key
interrupt pin (KR0 to KR9). The channel to which the valid edge was input can be identified by reading the port register
and checking the port level after the key interrupt (INTKR) is generated.
The INTKR signal changes according to the input level of the key interrupt input pin (KR0 to KR9).
Figure 17-7. Operation of INTKR Signal When a Key Interrupt is Input to a Single Channel
(When KRMD = 0 and KREG = 0)
KR0
INTKR
Delay
time
Note 1 Delay
time
Note 1
Note 2
KRIF
Notes 1. The maximum delay time is the maximum value of the high-level width and low-level width of the key
interrupt input (see 29.4 AC Characteristics and 30.4 AC Characteristics for details).
2. Acknowledgment of vectored interrupt request or bit cleared by software
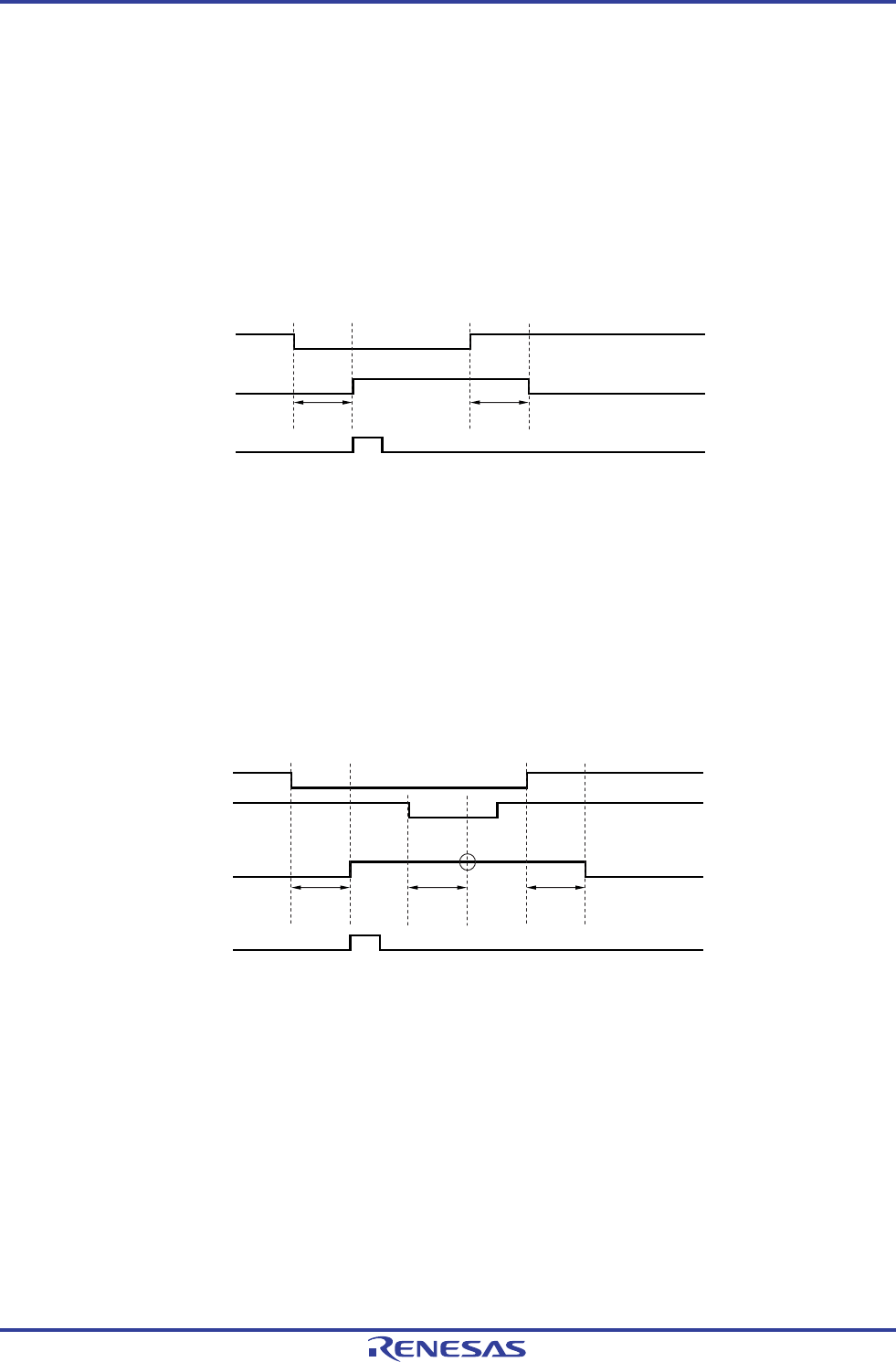
The operation when a valid edge is input to multiple key interrupt input pins is shown in Figure 17-8 below. The INTKR
signal is set while a low level is being input to one pin (when KREG is set to 0). Therefore, even if a falling edge is input to
another pin in this period, a key interrupt (INTKR) will not be generated again (<1> in the figure).
Figure 17-8. Operation of INTKR Signal When Key Interrupts Are Input to Multiple Channels
(When KRMD = 0 and KREG = 0)
KR0
KR1
<1>
INTKR
KRIF
Note 1Delay
time
Note 2
Note 1Delay
time
Note 1
Delay
time
Notes 1. The maximum delay time is the maximum value of the high-level width and low-level width of the key
interrupt input (see 29.4 AC Characteristics and 30.4 AC Characteristics for details).
2. Acknowledgment of vectored interrupt request or bit cleared by software
R01UH0305EJ0200 Rev.2.00 722
Jul 04, 2013