RL78/G1A CHAPTER 13 SERIAL INTERFACE IICA
13.5.2 Addresses
The address is defined by the 7 bits of data that follow the start condition.
An address is a 7-bit data segment that is output in order to select one of the slave devices that are connected to the
master device via the bus lines. Therefore, each slave device connected via the bus lines must have a unique address.
The slave devices include hardware that detects the start condition and checks whether or not the 7-bit address data
matches the data values stored in the slave address register 0 (SVA0). If the address data matches the SVA0 register
values, the slave device is selected and communicates with the master device until the master device generates a start
condition or stop condition.
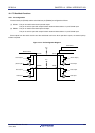
Figure 13-16. Address
SCLA0
SDAA0
INTIICA0
123456789
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
Address
Note
Note INTIICA0 is not issued if data other than a local address or extension code is received during slave device
operation.
Addresses are output when a total of 8 bits consisting of the slave address and the transfer direction described in
13.5.3 Transfer direction specification are written to the IICA shift register 0 (IICA0). The received addresses are
written to the IICA0 register.
The slave address is assigned to the higher 7 bits of the IICA0 register.
13.5.3 Transfer direction specification
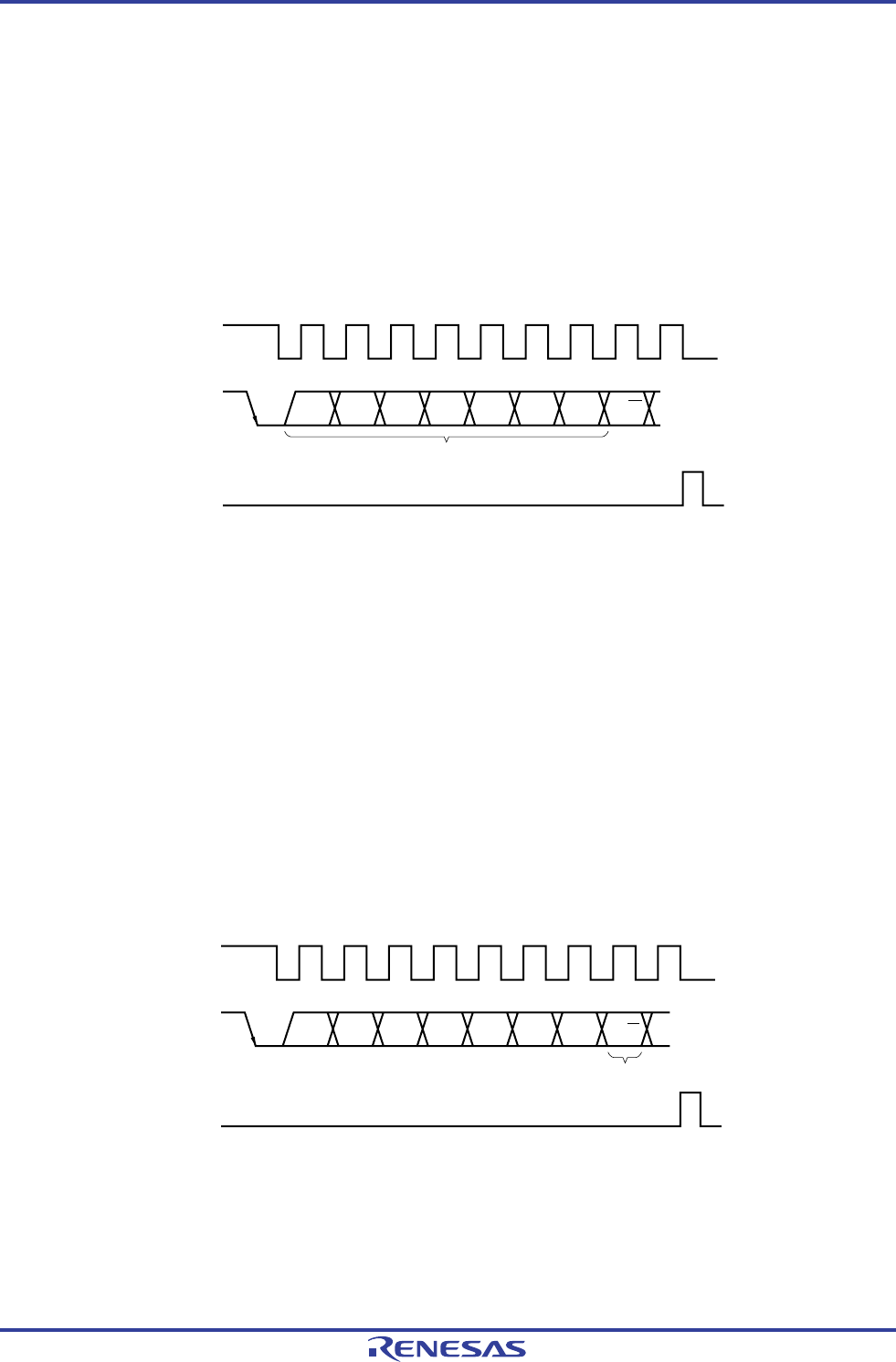
In addition to the 7-bit address data, the master device sends 1 bit that specifies the transfer direction.
When this transfer direction specification bit has a value of “0”, it indicates that the master device is transmitting data to
a slave device. When the transfer direction specification bit has a value of “1”, it indicates that the master device is
receiving data from a slave device.
Figure 13-17. Transfer Direction Specification
SCLA0
SDAA0
INTIICA0
123456789
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
Transfer direction specification
Note
Note INTIICA0 is not issued if data other than a local address or extension code is received during slave device
operation.
R01UH0305EJ0200 Rev.2.00 591
Jul 04, 2013