RL78/G1A CHAPTER 6 TIMER ARRAY UNIT
R01UH0305EJ0200 Rev.2.00 185
Jul 04, 2013
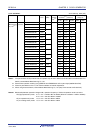
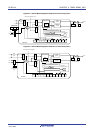
(6) Measurement of high-/low-level width of input signal
Counting is started by a single edge of the signal input to the timer input pin (TImn), and the count value is
captured at the other edge. In this way, the high-level or low-level width of the input signal can be measured.
Edge detection
Timer input
(TImn)
Capture
xxH
00H
Start
Channel n
Capture operation
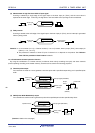
(7) Delay counter
Counting is started at the valid edge of the signal input to the timer input pin (TImn), and an interrupt is generated
after any delay period.
Edge detection
Timer input
(TImn)
Channel n
Compare operation
Interrupt signal
(INTTMmn)
Start
Remarks 1 m: Unit number (m = 0), n: Channel number (n = 0 to 7 (however, timer input pin (TImn), timer output pin
(TOmn) : n = 0, 1, 3 to 7))
2. The presence or absence of timer I/O pins of channel 0 to 7 depends on the product. See Table 6-2
Timer I/O Pins provided in Each Product for details.
6.1.2 Simultaneous channel operation function
By using the combination of a master channel (a reference timer mainly controlling the cycle) and slave channels
(timers operating according to the master channel), channels can be used for the following purposes.
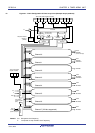
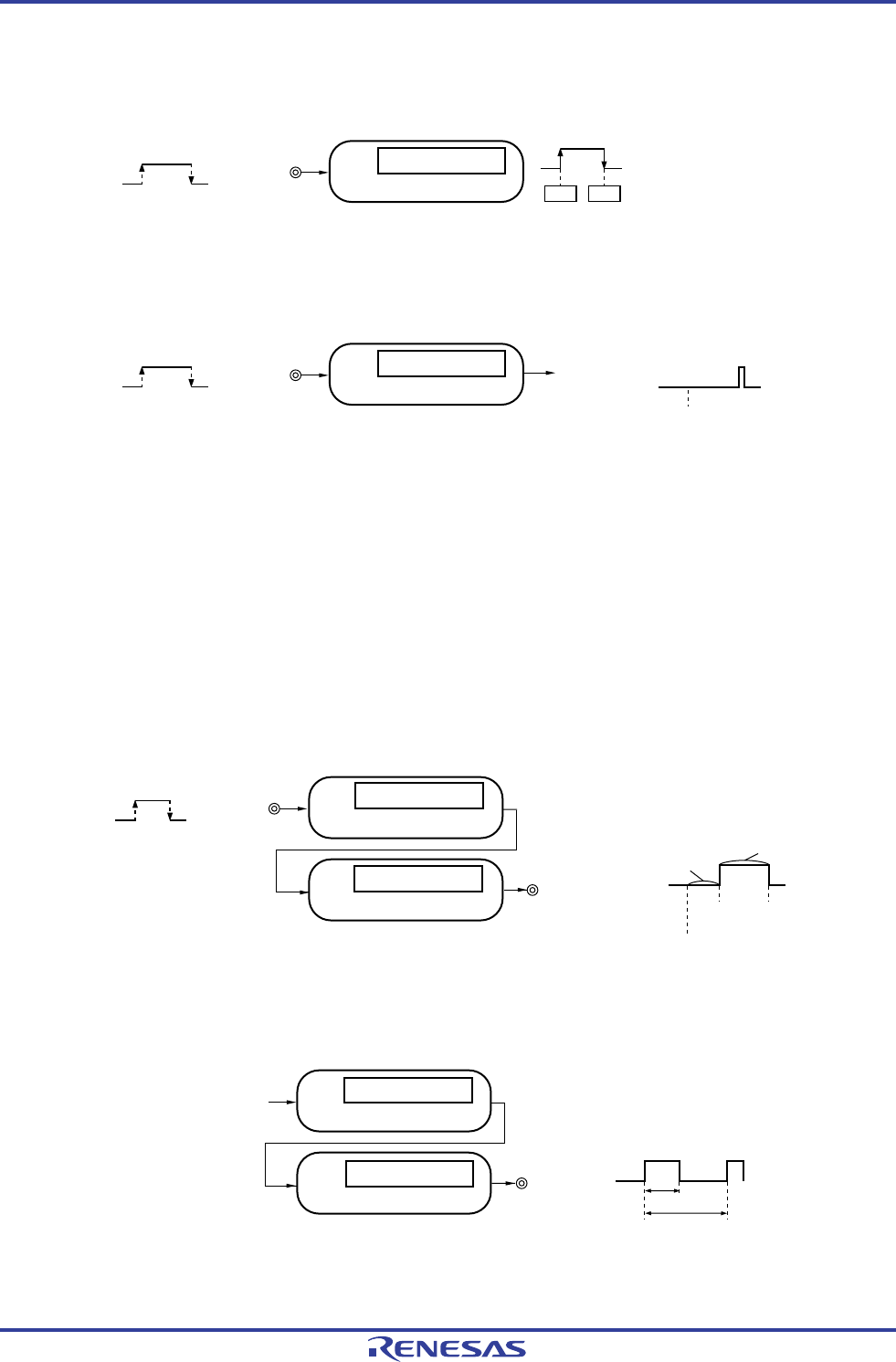
(1) One-shot pulse output
Two channels are used as a set to generate a one-shot pulse with a specified output timing and a specified pulse
width.
Timer output
(TOmp)
Interrupt signal (INTTMmn)
Edge detection
Timer input
(TImn)
Set
(Master)
Output
timing
Pulse width
Start
(Master)
Reset
(Slave)
Channel n (master)
Channel p (slave)
Compare operation
Compare operation
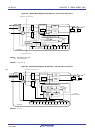
(2) PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) output
Two channels are used as a set to generate a pulse with a specified period and a specified duty factor.
Operation clock
Duty
Period
Compare operation
Compare operation
Channel n (master)
Channel p (slave)
Timer output
(TOmp)
Interrupt signal (INTTMmn)
(Caution is listed on the next page.)
<R>