5 - 42
5 Servo Adjustment
MITSUBISHI CNC
5.3.7 Improvement of the Interpolation Control Path
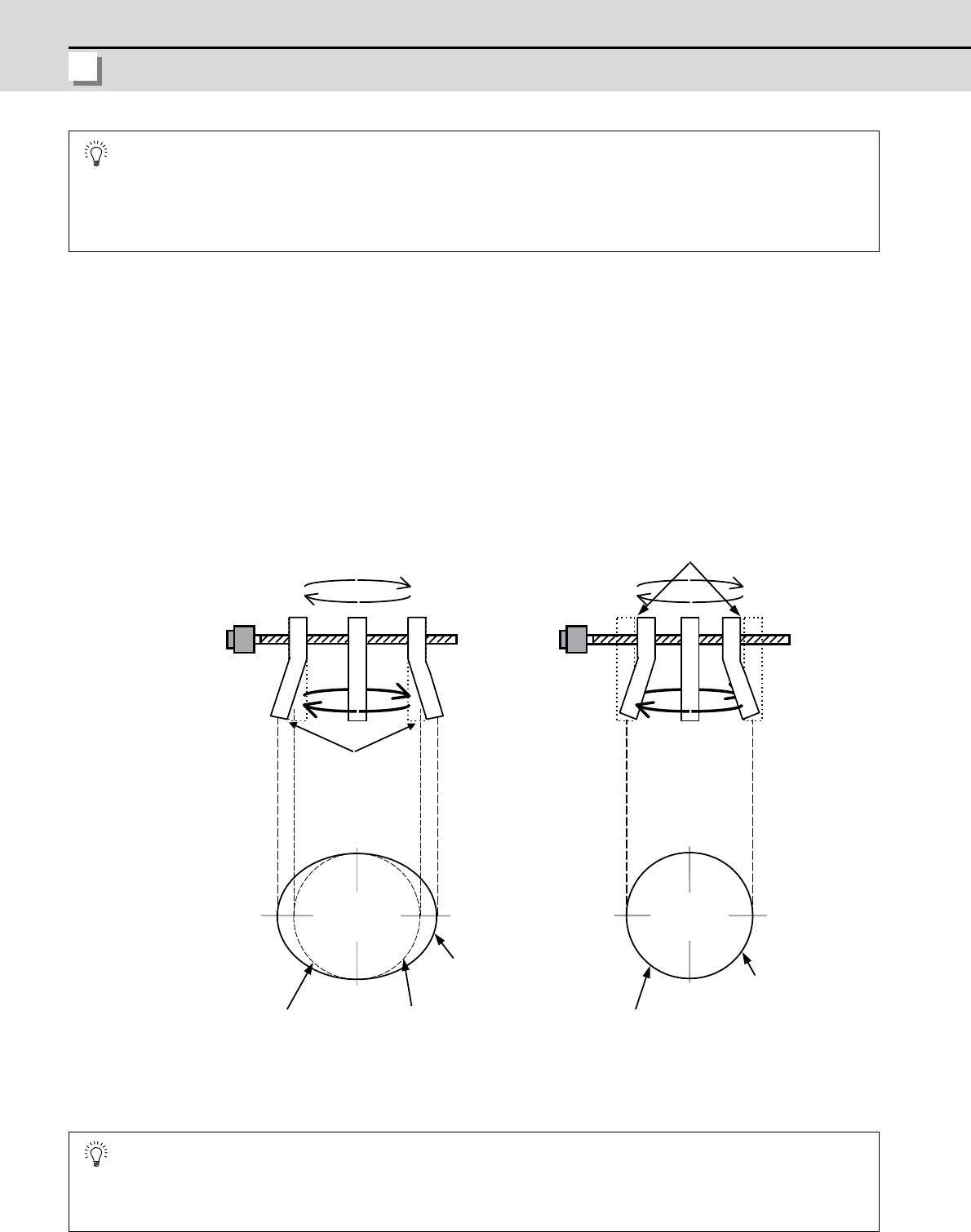
(1) Machine end compensation control
The machine end compensation control compensates the shape of the tool end during high-speed and high-speed
acceleration/deceleration. The spring effect from the machine (spindle) end to the motor (scale) end is
compensated. If the machine has a large spring effect, the shape may be fine during low-speed operation.
However, at high speeds (specially when using a small radius), the section from the machine (spindle) end to the
outer sides of the motor (scale) end could swell, and cause the shape to become elliptical during measurement of
the roundness. The machine end compensation control compensates the motor end position according to the
acceleration size, so the tool end position is always controlled to the commanded position.
POINT
When using feed forward control (high-speed high-accuracy control), stop the feed forward control (fwd_g=0)
before adjusting the overshooting compensation. If overshooting occurs during subsequent feed forward control,
adjust the feed forward gain (fwd_g).
POINT
1. Always evaluate the roundness accuracy at the machine side.
2. Adjust the parameter after adjusting the electrical end roundness accuracy.
With machine end compensation control
During high acceleration,
the end section swells
outward due to the spring
effect.
The inner side is driven by the
amount that the end section swells
due to the spring effect.
Machine
roundness
(machining
surface)
Elliptical shape
fault
Machine
roundness
(machining
surface)
Elliptical shape is
improved
Low speed:
Example:
R25mm
F1000mm/min
High speed
(high acceleration):
Example:
R25mm
F10000mm/min
B
o
th
l
ow spee
d
an
d
high speed are on
the same path.
Command path
(ideal path)
Machine path
(machining surface)
Machine path
(machining surface)
Command path
(ideal path)
Without machine end compensation control


















