Introduction 547
SmartWare Software Configuration Guide 45 • H.323 gateway configuration
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the H.323 gateway and describes the tasks involved in its configuration.
A gateway is always needed when communication is required between different networks. A gateway provides:
• Data format translation, e.g. audio and video CODEC translation
• Control signaling translation, e.g. call setup and tear-down functionality on both sides of a network.
The gateway manages connections between two different contexts, essentially functioning as a protocol con-
verter. Additionally it also contains general gateway configuration parameters.
One type of gateway is the H.323 gateway and is an implementation of the ITU-T H.323 Version 4 standard.
The H.323 gateway has bindings to interfaces on the two different contexts. The CS Context has H.323 CS
interfaces and the IP context has IP interfaces. The H.323 CS interfaces are explained in detail in chapter 38,
“H.323 interface configuration” on page 431.
The H.323 interfaces in the CS context must be explicitly bound to a H.323 gateway instance, and the H.323
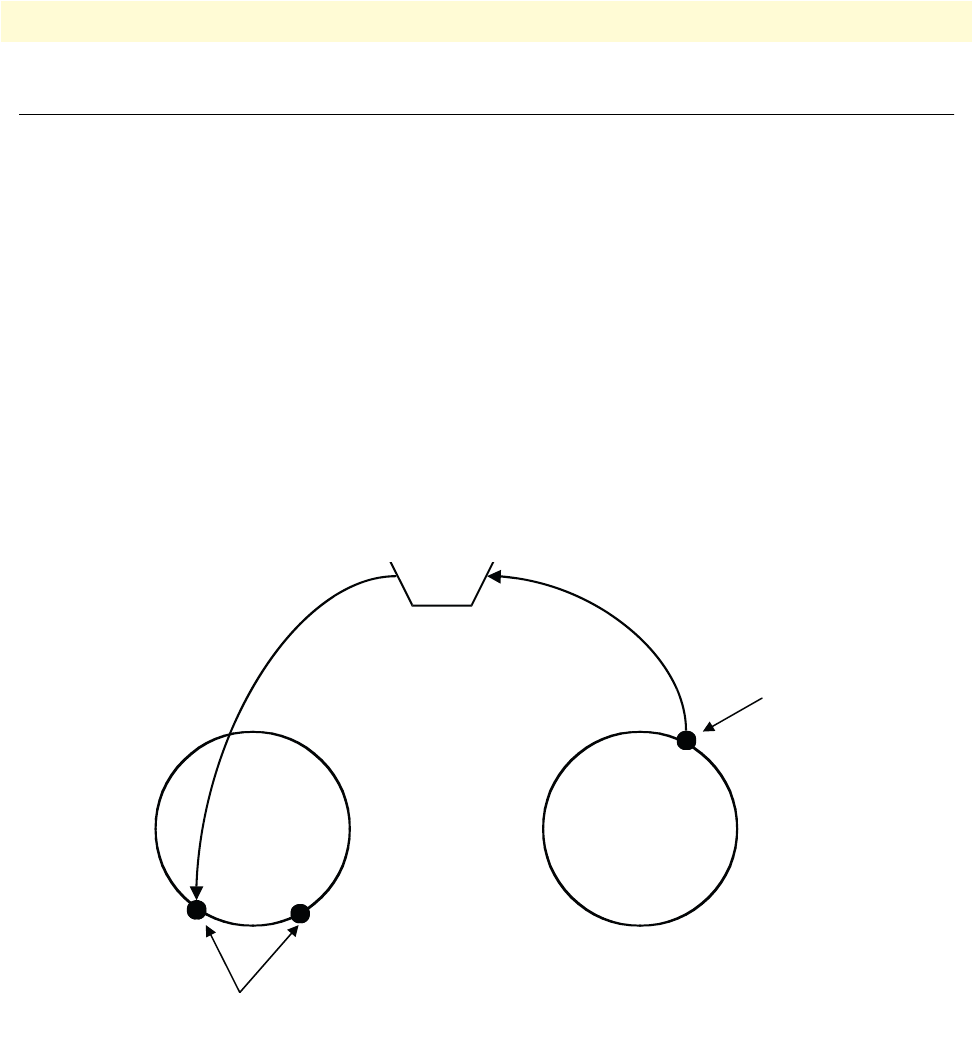
gateway must be bound explicitly to an IP interface in the IP context. Figure 77 illustrates the relationship of
the H.323 gateway to the contexts and their interfaces.
Figure 77. Gateway between IP and CS contexts
SmartWare currently supports only one instance of the H.323 gateway. The default name of the H.323 gate-
way is h323. The H.323 gateway is enabled by default.
bind interface
bind gateway
H.323
Interface
H
.
323
Gateway
Context IP
“router”
IP interfaces
Context CS
“switch”


















