Setting access community information 272
SmartWare Software Configuration Guide 25 • SNMP configuration
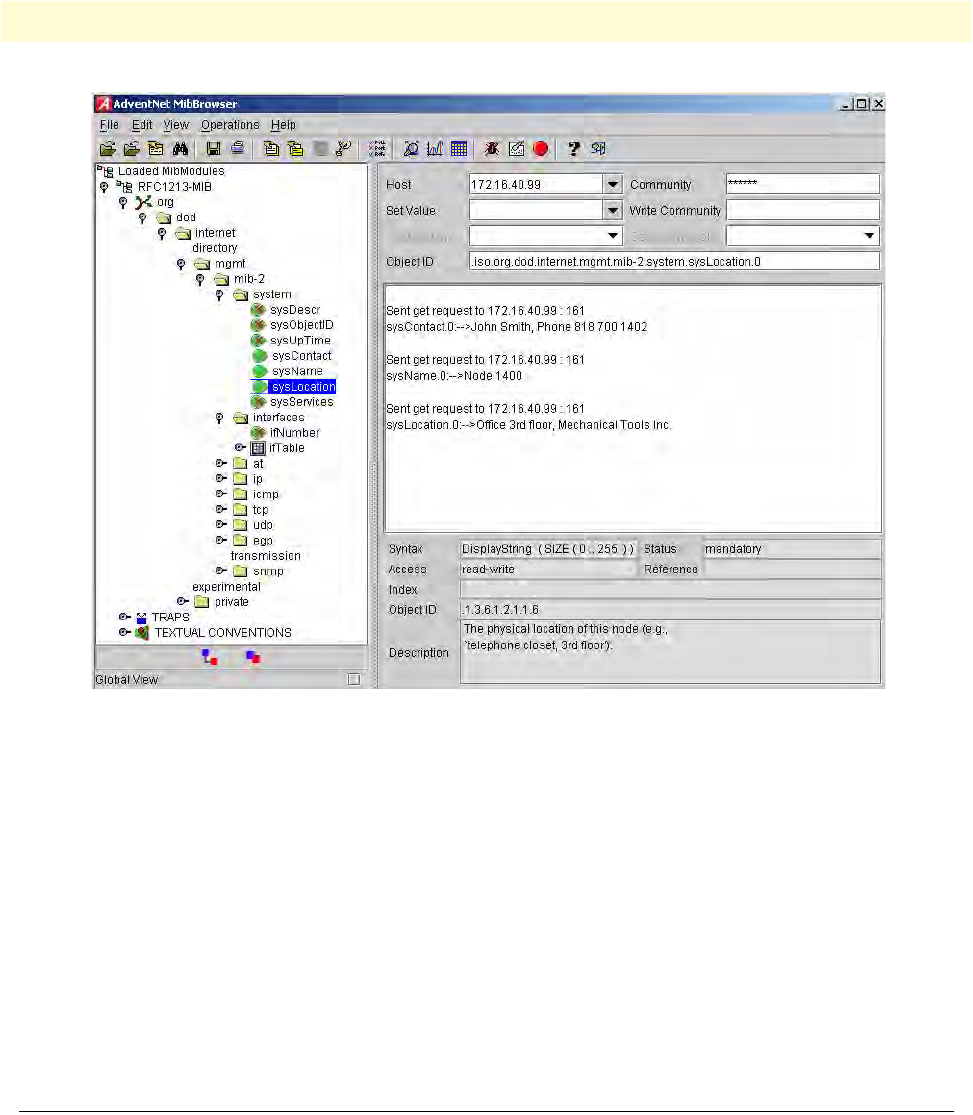
Figure 40. AdventNet MibBrowser displaying some of the System Group objects
Example: Setting the system group objects
In the following example the system information is set for later access via SNMP. See figure 40 for a typical
MIB browser application accessing these MIB-II system group objects representing the system information.
node>enable
node#configure
node(cfg)#system contact "Bill Anybody, Phone 818 700 1504"
node(cfg)#system location "Wiring Closet, 3rd floor"
node(cfg)#system hostname "node"
(cfg)#
After entering a host name the prompt on the CLI no longer displays the IP address of the Ethernet port over
which the Telnet session is running but shows the newly entered host name.
Setting access community information
SNMP uses one or more labels called community strings to delimit groups of objects (variables) that can be
viewed or modified on a device. The SNMP data in such a group is organized in a tree structure called a Man-
agement Information Base (MIB). A single device may have multiple MIBs connected together into one large
structure, and various community strings may provide read-only or read-write access to different, possibly
overlapping portions of the larger data structure. An example of a read-only variable might be a counter show-
ing the total number of octets sent or received through an interface. An example of a read-write variable might
be the speed of an interface, or the hostname of a device.