Examples 240
SmartWare Software Configuration Guide 22 • Basic IP routing configuration
In this routing table two default routes (0.0.0.0/0) are defined. The first default route is valid for packets of the
class local-voice only. The second default route is valid for all packets. Thus voice packets generated locally
(traffic-class local-voice) will travel via the gateway (Nexthop) 172.16.32.1. All other packets will travel via the
gateway (Nexthop) 172.16.32.2.
NOTE: If the second default route was missing, there would be no default route for packets of traffic-class
other than local-voice.
The following modified commands are used with policy routing:
Route—refer to the ‘route’ command in the subsection “Configuring static IP routes” on page 237 in this
chapter.
Ping—refer to the ‘ping’ command described in the subsection “Testing connections with the ping command”
on page 127 in Chapter 10: IP interface configuration.
Traceroute—refer to the ‘traceroute’ command described in the subsection “Traceroute” on page 130 in Chap-
ter 10: IP interface configuration.
Examples
Basic static IP routing example
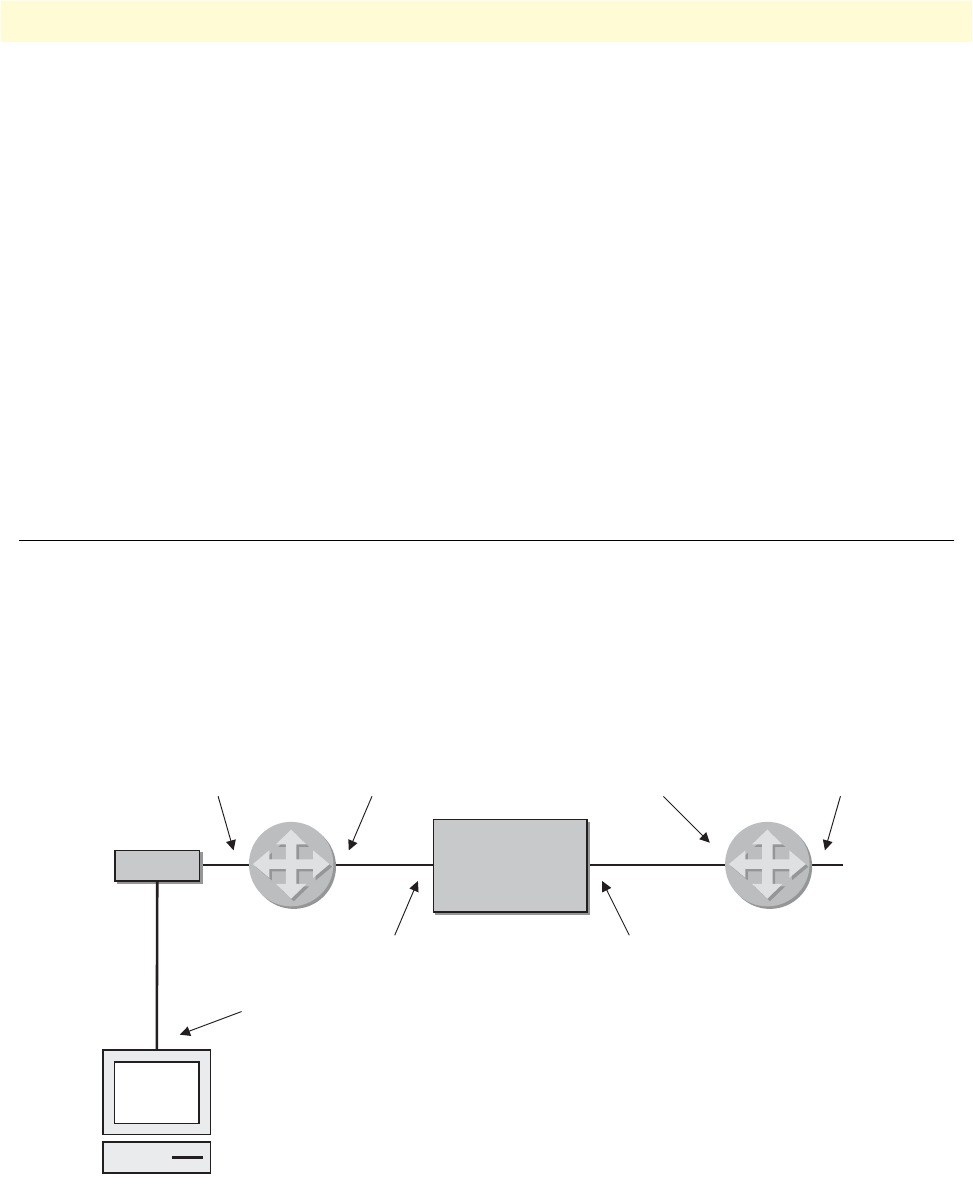
Figure 37 shows an Internetwork consisting of three routers, a SmartNode device in the middle, and the four
autonomous networks, with network addresses 10.1.5.0/16, 172.16.40.0/24, 172.17.100.0/24, and 10.2.5.0/
16. The SmartNode shall be configured for the following IP routing scenario:
All packets for the Workstation with IP address 10.1.5.10 shall be forwarded to the next-hop router Calvin. All
packets for network 10.2.5.0/16 shall be forwarded to the next-hop router Hobbes.
Figure 37. Internetwork with three routers and four networks
Node
Node
172.17.100.2/24
172.17.100.1/24172.16.40.1/24
172.16.40.2/2410.1.5.2/16 10.2.5.2/16
lan wan
Calvin
Hobbes
Hub
Hub
10.1.5.10/16
Workstation


















