NAT/NAPT configuration task list 137
SmartWare Software Configuration Guide 11 • NAT/NAPT configuration
Use no in front of the above commands to delete a specific entry or the whole profile.
Note The command icmp default is obsolete.
Example: Creating a NAPT Profile
The following example shows how to create a new NAPT profile access that contains all settings necessary to
implement the examples in section “Introduction” on page 133.
node(cfg)#profile napt access
node(pf-napt)[access]#range 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.19 131.1.1.2
node(pf-napt)[access]#static tcp 192.168.1.20 80
node(pf-napt)[access]#static tcp 192.168.1.20 23 131.1.1.3
node(pf-napt)[access]#range 192.168.1.30 192.168.1.39 131.1.1.10 131.1.1.15
node(pf-napt)[access]#static 192.168.1.40 131.1.1.20
node(pf-napt)[access]static ah 192.168.1.41 131.1.1.120
Configuring a NAPT DMZ host
The NAPT allows a DMZ host to be configured, which receives any inbound traffic on the global NAPT
interface, which:
• Is not translated by any static or dynamic NAPT entry and
• Is not handled by the device itself.
The following procedure shows how a DMZ host can be configured.
Mode: profile napt <pf-name>
Defining NAPT port ranges
The TCP/UDP port ranges to be used by the NAPT can be defined using the following procedure. The default
port ranges for both TCP/UDP are 8000 to 15999.
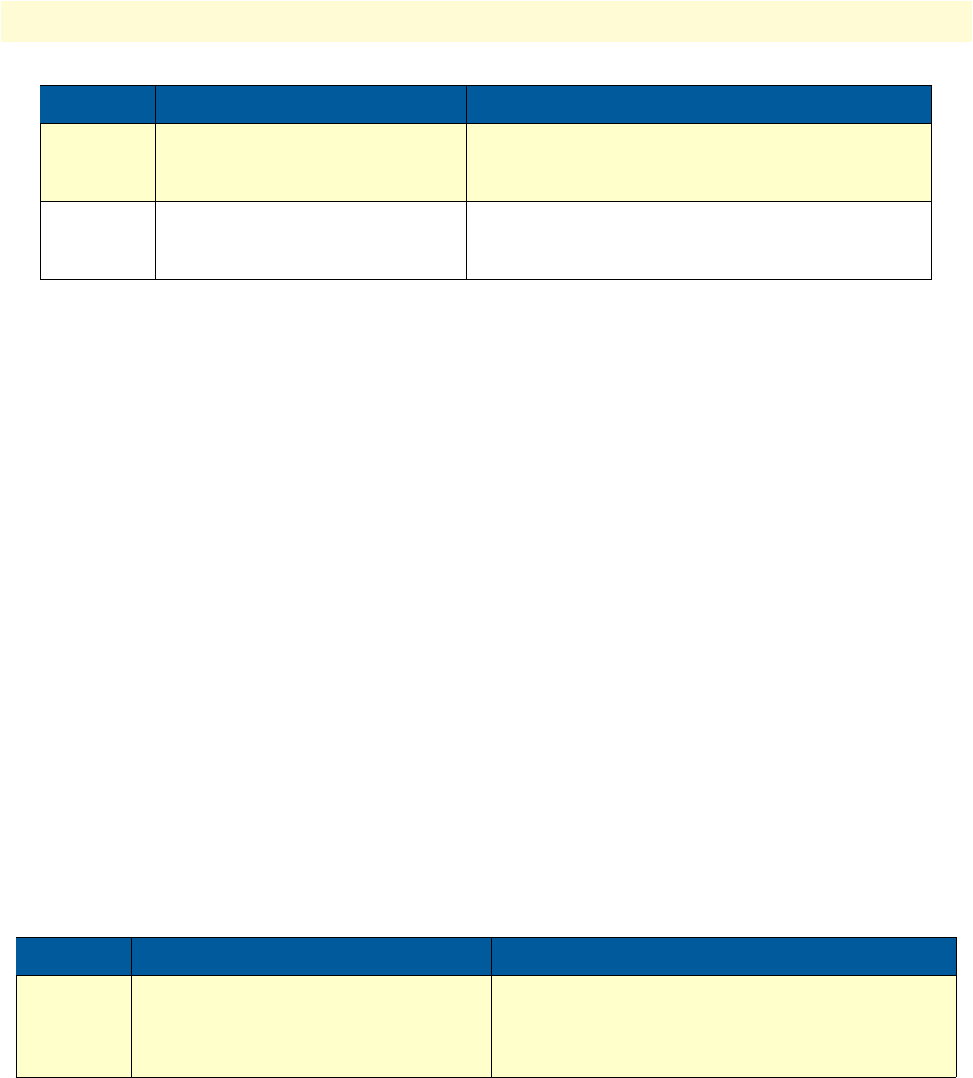
5
(optional)
node(pf-napt)[name]#static local-
ip global-ip
Creates a Static NAT entry: local-ip is mapped to
global-ip.
(max. 20 entries)
6
(optional)
node(pf-napt)[name]#static
{ ah|esp|gre|ipv6 } local_ip
[global_ip].
Creates a static NAT entry: traffic of the IP protocol
AH, ESP, GRE, or IPv6 respectively directed to the
global_ip is forwarded to the local_ip.
Step Command Purpose
1 [name] (pf-napt)[pf-name]# [no]
dmz-host <dmz-host-ip-address>
[<global-ip-address>]
Configures a DMZ host. The global-ip-address must
only be specified, if the DMZ host shall handle the
inbound traffic for a different NAPT global IP address
than the gateways global interface IP address.
Step Command Purpose


















