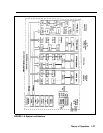
ANALOG TO DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESSING
Analog to Digital
Signal Conversion
processor. The port processor directs Touch-Tone
circuitry to output tones. The tones are placed on the
TDM bus by the DSE through buffer circuitry. After a
tip condition occurs at the remote end, a conversation
may occur.
The MERLIN II system receives analog signals from the
central office lines and analog modules. In order to be
switched, the analog signals must be converted to digital
signals. Digital transmissions have several advantages
over analog transmissions. They produce superior bit
error rates and have lower noise/signal degradation,
simpler circuitry in some cases, and greater flexibility.
They also have various performance advantages, such as
speed and a nonblocking architecture.
If an analog signal is sampled in increments equivalent to
twice the frequency of that signal, then the sample can
faithfully reproduce the signal at a digital level.
The first step in analog to digital conversion is to sample
the pulse amplitude of the analog signal. Then the sample
is converted into a series of amplitude steps. This
technique is referred to as Pulse Amplitude Modulation
(PAM). Analog to digital converters (codecs) are an
integral part of voice and data systems. Codecs use a
variety of encoding techniques. The MERLIN II system
uses Pulse Code Modulation (PCM).
The process of converting an analog signal to a digital
level increases the capacity and efficiency of data
transmissions. However, a digitized analog signal retains
some of the problems of older transmission systems, such
as having to be amplified.
1-40 Theory of Operation