Configuring Router-Port Group Management Protocol
RGMP Overview
IPC-529
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
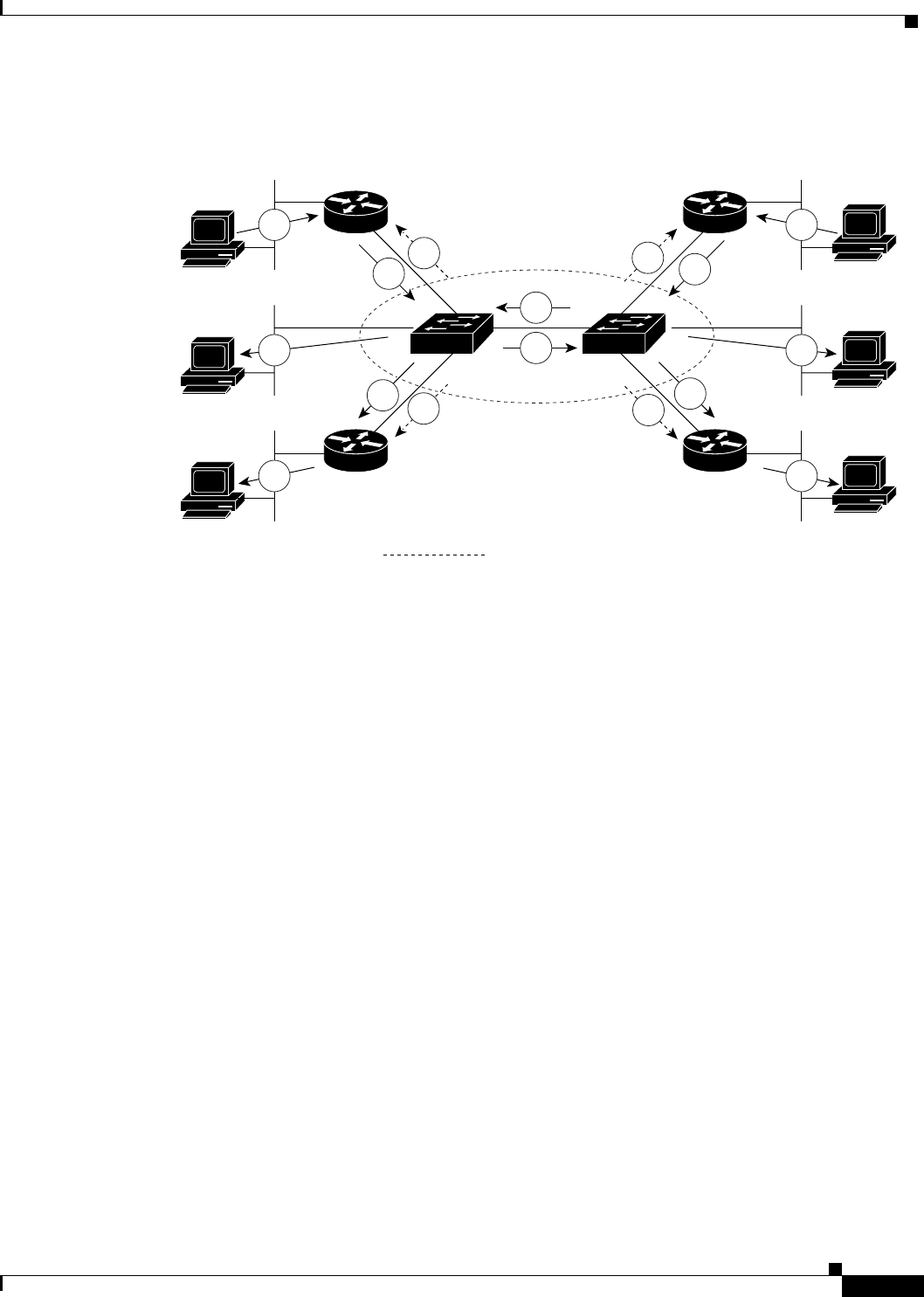
Figure 89 RGMP in a Switched Network
In Figure 89, the sources for the two different multicast groups (the source for group A and the source
for group B) send traffic into the same switched network. Without RGMP, traffic from source A is
unnecessarily flooded from switch A to switch B, then to router B and router D. Also, traffic from
source B is unnecessarily flooded from switch B to switch A, then to router A and router C. With RGMP
enabled on all routers and switches in this network, traffic from source A would not flood router B and
router D. Also, traffic from source B would not flood router A and router C. Traffic from both sources
would still flood the link between switch A and switch B. Flooding over this link would still occur
because RGMP does not restrict traffic on links toward other RGMP-enabled switches with routers
behind them.
By restricting unwanted multicast traffic in a switched network, RGMP increases the available
bandwidth for all other multicast traffic in the network and saves the processing resources of the routers.
Figure 90 shows the RGMP messages sent between an RGMP-enabled router and an RGMP-enabled
switch.
A
B
B
B
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
A
A
Source for
group A
Router A
PIM SM
RGMP
Switch A
RGMP
IGMP
Switch B
RGMP
IGMP
Switch A
RGMP
IGMP
snooping
Switch B
RGMP
IGMP
snooping
Router C
PIM SM
RGMP
Router B
PIM SM
RGMP
Router D
PIM SM
RGMP
Switched network
Traffic restricted by RGMP
Receiver 1
for group A
Receiver 2
for group A
Source for
group B
Receiver 1
for group B
Receiver 2
for group B
A
A
39165