Configuring Mobile IP
Mobile IP Overview
IPC-160
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
IP routing decisions are based on the network prefix of the IP address to be scalable for the Internet. All
nodes on the same link share a common network prefix. If a node moves to another link, the network
prefix does not equal the network prefix on the new link. Consequently, IP routing would fail to route
the packets to the node after movement to the new link.
An alternative to network-prefix routing is host-specific routing. Host-specific routing is not a problem
in small networks. However, considering there are billions of hosts on the Internet, this solution is not
feasible for Internet connections. Routers would need enough memory to store tens of millions of routing
table entries and would spend most of their computing resources updating routing tables.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is commonly used in corporate environments and allows
a server to dynamically assign IP addresses and deliver configuration parameters to nodes. The DHCP
Server verifies the identity of the node, “leases” it the IP address from a pool of addresses for a
predetermined period of time, and reclaims the address for reassignment when the lease expires. The
node can terminate existing communication sessions, move to a new point-of-attachment to the network,
reconnect to the network, and receive a new IP address from DHCP. This arrangement conserves IP
addresses and reduces Internet access costs. However, if users are mobile and need continuous
communications and accessibility without any interruptions in their sessions, DHCP is not an adequate
solution. DHCP won’t allow applications to maintain connections across subnet/network boundaries.
Mobile IP is scalable for the Internet because it is based on IP—any media that supports IP can support
Mobile IP. Mobile IP does not drop the network prefix of the IP address of the node, which is critical to
the proper routing of packets throughout the Internet. Also, certain network services, such as software
licenses and access privileges, are based on IP addresses. Changing these IP addresses could
compromise the network services. Certain applications, such as remote login, remote printing, and file
transfers are examples of applications where it is undesirable to interrupt communications while a
mobile node moves from one link to another. Thus, Mobile IP provides the solution for continuous
connectivity that is scalable for the Internet.
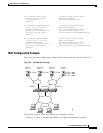
Mobile IP Components
Mobile IP is comprised of the following three components, as shown in Figure 27:
• Mobile node (MN)
• Home agent (HA)
• Foreign agent (FA)