Configuring IP Addressing
Configuring Address Resolution Methods
IPC-19
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
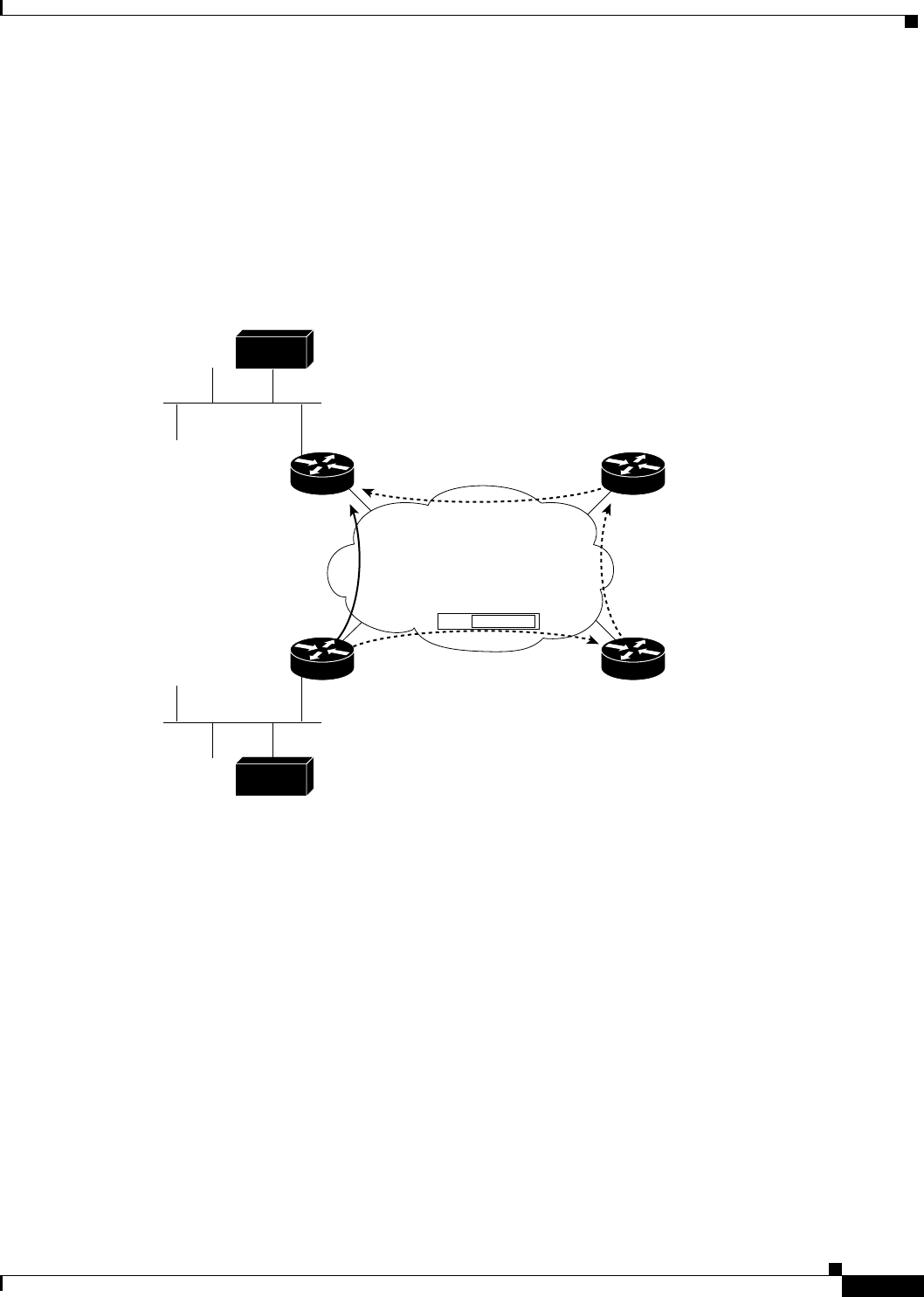
Figure 3 illustrates four routers connected to an NBMA network. Within the network are ATM or SMDS
switches necessary for the routers to communicate with each other. Assume that the switches have virtual
circuit (VC) connections represented by hops 1, 2, and 3 of the figure. When Router A attempts to
forward an IP packet from the source host to the destination host, NHRP is triggered. On behalf of the
source host, Router A sends an NHRP request packet encapsulated in an IP packet, which takes three
hops across the network to reach Router D, connected to the destination host. After receiving a positive
NHRP reply, Router D is determined to be the “NBMA next hop,” and Router A sends subsequent IP
packets for the destination to Router D in one hop.
Figure 3 Next Hop Resolution Protocol
With NHRP, once the NBMA next hop is determined, the source either starts sending data packets to the
destination (in a connectionless NBMA network such as SMDS) or establishes a virtual circuit VC
connection to the destination with the desired bandwidth and quality of service (QoS) characteristics (in
a connection-oriented NBMA network such as ATM).
Other address resolution methods can be used while NHRP is deployed. IP hosts that rely upon the
Logical IP Subnet (LIS) model might require ARP servers and services over NBMA networks, and
deployed hosts might not implement NHRP, but might continue to support ARP variations. NHRP is
designed to eliminate the suboptimal routing that results from the LIS model, and can be deployed with
existing ARP services without interfering with them.
NHRP is used to facilitate building a Virtual Private Network (VPN). In this context, a VPN consists of
a virtual Layer 3 network that is built on top of an actual Layer 3 network. The topology you use over
the VPN is largely independent of the underlying network, and the protocols you run over it are
completely independent of it.
Connected to the NBMA network are one or more stations that implement NHRP, and are known as Next
Hop Servers. All routers running Cisco IOS Release 10.3 or later releases can implement NHRP and,
thus, can act as Next Hop Servers.
Router D
Source
host
Router C
Router A
Router B
IP NHRP
Hop 1
Hop 2
Hop 3
Subsequent
IP packets
NBMA network
NBMA next hop
Destination
host
S3229


















