Configuring IP Multicast Routing
Configuring RTP Header Compression
IPC-431
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
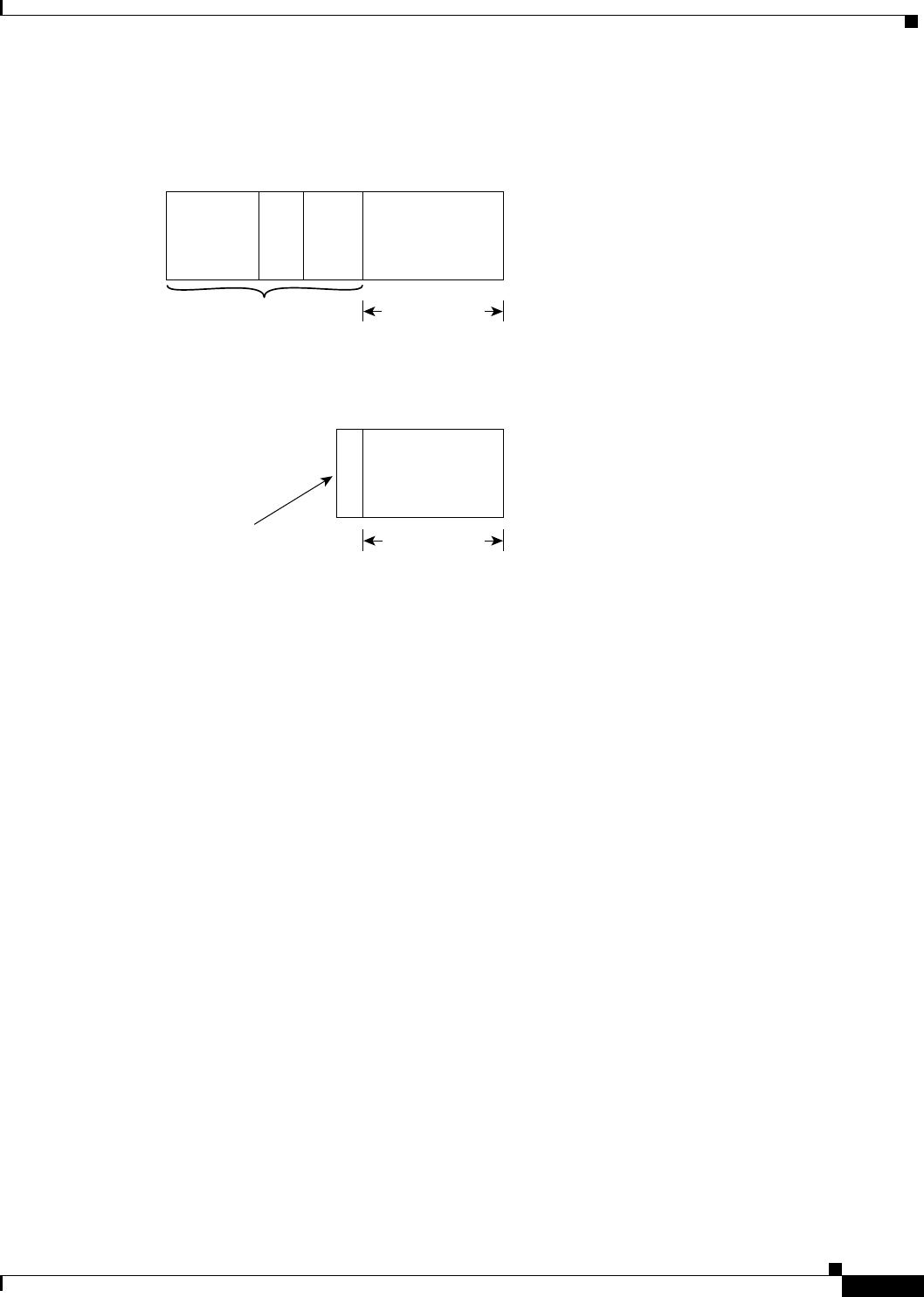
Figure 70 RTP Header Compression
The RTP header compression feature compresses the IP/UDP/RTP header in an RTP data packet from
40 bytes to approximately 2 to 5 bytes, as shown in Figure 70. It is a hop-by-hop compression scheme
similar to RFC 1144 for TCP/IP header compression. Using RTP header compression can benefit both
telephony voice and MBONE applications running over slow links.
RTP header compression is supported on serial lines using Frame Relay, High-Level Data Link Control
(HDLC), or PPP encapsulation. It is also supported over ISDN interfaces.
Enabling compression on both ends of a low-bandwidth serial link can greatly reduce the network
overhead if substantial amounts of RTP traffic are on that slow link. This compression is beneficial
especially when the RTP payload size is small (for example, compressed audio payloads of 20 to 50
bytes). Although the MBONE-style RTP traffic has higher payload sizes, compact encodings such as
code excited linear prediction (CELP) compression can also help considerably.
Before you can enable RTP header compression, you must have configured a serial line that uses either
Frame Relay, HDLC, or PPP encapsulation, or an ISDN interface. To configure RTP header
compression, perform the tasks described in the following sections. Either one of the first two tasks is
required.
• Enabling RTP Header Compression on a Serial Interface
• Enabling RTP Header Compression with Frame Relay Encapsulation
• Changing the Number of Header Compression Connections
You can compress the IP/UDP/RTP headers of RTP traffic to reduce the size of your packets, making
audio or video communication more efficient. You must enable compression on both ends of a serial
connection.
RTP header compression occurs in either the fast-switched or CEF-switched path, depending on whether
certain prerequisites are met. Otherwise, it occurs in the process-switched path. For more information
about where RTP header compression occurs, see the section “Enabling Express RTP Header
Compression” later in this document.
Before RTP header compression:
20 bytes 8 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
12 bytes
IP
Header
UDP
RTP Payload
After RTP header compression:
3 to 5 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
IP/UDP/RTP header
Payload
S5925


















