Configuring IP Routing Protocol-Independent Features
IP Routing Protocol-Independent Configuration Examples
IPC-392
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
See more route map examples in the “BGP Route Map Examples” and “BGP Community with Route
Maps Examples” sections of the 12.4 BGP documentation.
Passive Interface Examples
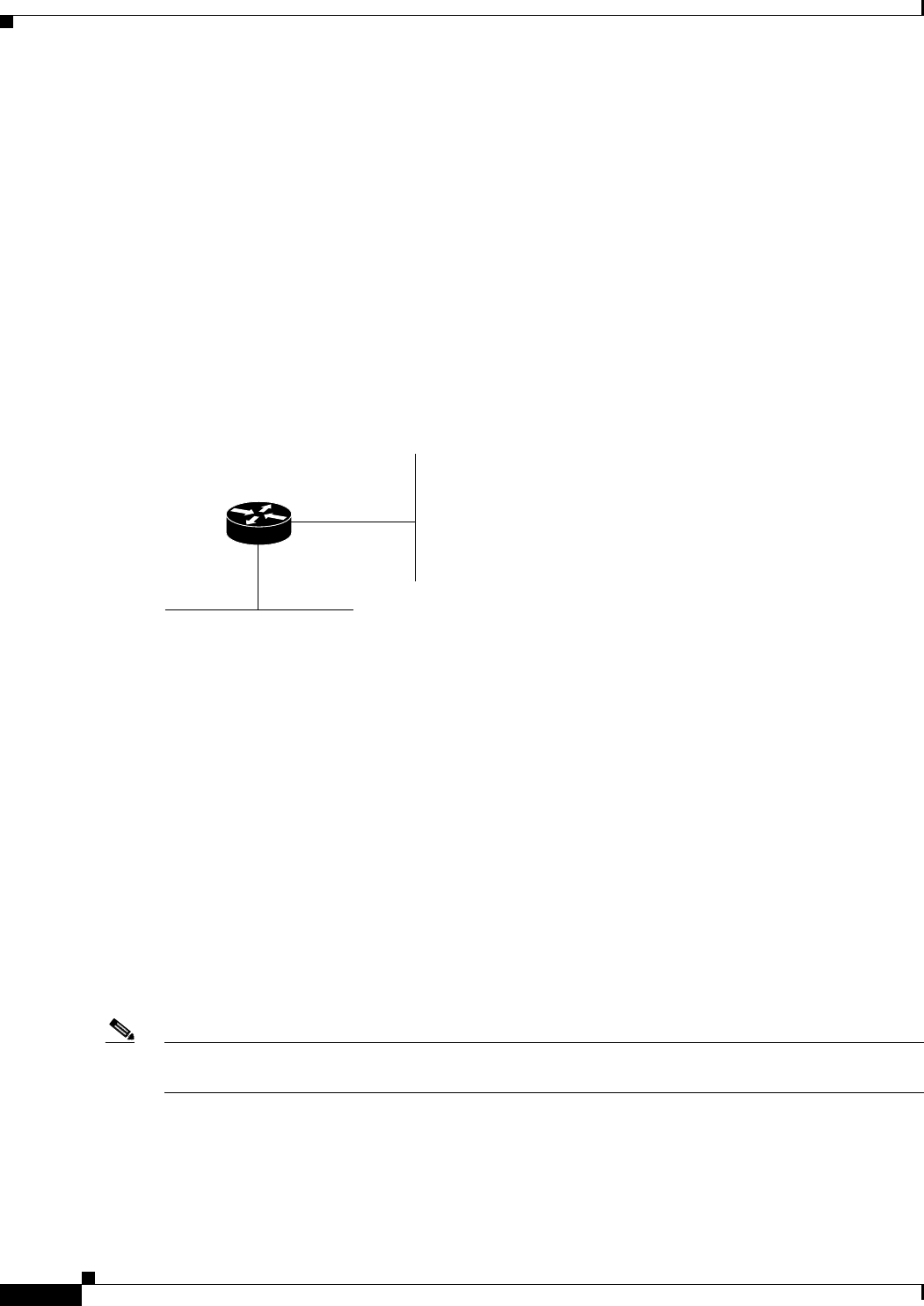
The following example configures Ethernet interface 1 as a passive interface under IGRP. Figure 65
shows the router topology. Routing updates are sent out all interfaces in the 192.168/16 network except
for Ethernet interface 1.
interface Ethernet 1
ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.0.0
router igrp 1
network 192.168.0.0
passive-interface Ethernet 1
Figure 65 Filtering IGRP Updates
In the following example, as in the first example, IGRP updates are sent out all interfaces in the
192.168/16 network except for Ethernet interface 1. However, in this configuration a neighbor statement
is configured explicitly for the 192.168.0.2 neighbor. This neighbor statement will override the
passive-interface configuration, and all interfaces in the 192.168/16 network, including Ethernet
interface 1, will send routing advertisements to the 192.168.0.2 neighbor.
router igrp 1
network 192.168.0.0
passive-interface ethernet 1
neighbor 192.18.0.2
The passive-interface command disables the transmission and receipt of EIGRP hello packets on an
interface. Unlike IGRP or RIP, EIGRP sends hello packets in order to form and sustain neighbor
adjacencies. Without a neighbor adjacency, EIGRP cannot exchange routes with a neighbor. Therefore,
the passive-interface command prevents the exchange of routes on the interface. Although EIGRP does
not send or receive routing updates on an interface configured with the passive-interface command, it
still includes the address of the interface in routing updates sent out of other nonpassive interfaces.
Note For more information about configuring passive interfaces in EIGRP, see the How Does the Passive
Interface Feature Work in EIGRP? document on cisco.com.
In OSPF, hello packets are not sent on an interface that is specified as passive. Hence, the router will not
be able to discover any neighbors, and none of the OSPF neighbors will be able to see the router on that
network. In effect, this interface will appear as a stub network to the OSPF domain. This configuration
is useful if you want to import routes associated with a connected network into the OSPF domain without
any OSPF activity on that interface.
IGRP router
S1067a
E1
No routing updates
sent to this interface


















