Configuring IP Multicast Routing
Configuring an IP Multicast Boundary
IPC-438
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
Configuring an IP Multicast Boundary
You can set up an administratively scoped boundary on an interface for multicast group addresses. A
standard access list defines the range of addresses affected. When a boundary is set up, no multicast data
packets are allowed to flow across the boundary from either direction. The boundary allows the same
multicast group address to be reused in different administrative domains.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has designated the multicast address range 239.0.0.0
to 239.255.255.255 as the administratively scoped addresses. This range of addresses can be reused in
domains administered by different organizations. They would be considered local, not globally unique.
You can configure the filter-autorp keyword to examine and filter Auto-RP discovery and
announcement messages at the administratively scoped boundary. Any Auto-RP group range
announcements from the Auto-RP packets that are denied by the boundary access control list (ACL) are
removed. An Auto-RP group range announcement is permitted and passed by the boundary only if all
addresses in the Auto-RP group range are permitted by the boundary ACL. If any address is not
permitted, the entire group range is filtered and removed from the Auto-RP message before the Auto-RP
message is forwarded.
To set up an administratively scoped boundary, use the following commands beginning in global
configuration mode:
See the section “Administratively Scoped Boundary Example” later in this chapter for an example of
configuring a boundary.
Configuring an Intermediate IP Multicast Helper
When a multicast-capable internetwork is between two subnets with broadcast-only-capable hosts, you
can convert broadcast traffic to multicast at the first hop router, and convert it back to broadcast at the
last hop router to deliver the packets to the broadcast clients. Thus, you can take advantage of the
multicast capability of the intermediate multicast internetwork. Configuring an intermediate IP multicast
helper prevents unnecessary replication at the intermediate routers and can take advantage of multicast
fast switching in the multicast internetwork.
See Figure 73 and the example of this feature in the section “IP Multicast Helper Example” later in this
chapter.
An extended IP access list controls which broadcast packets are translated, based on the UDP port
number.
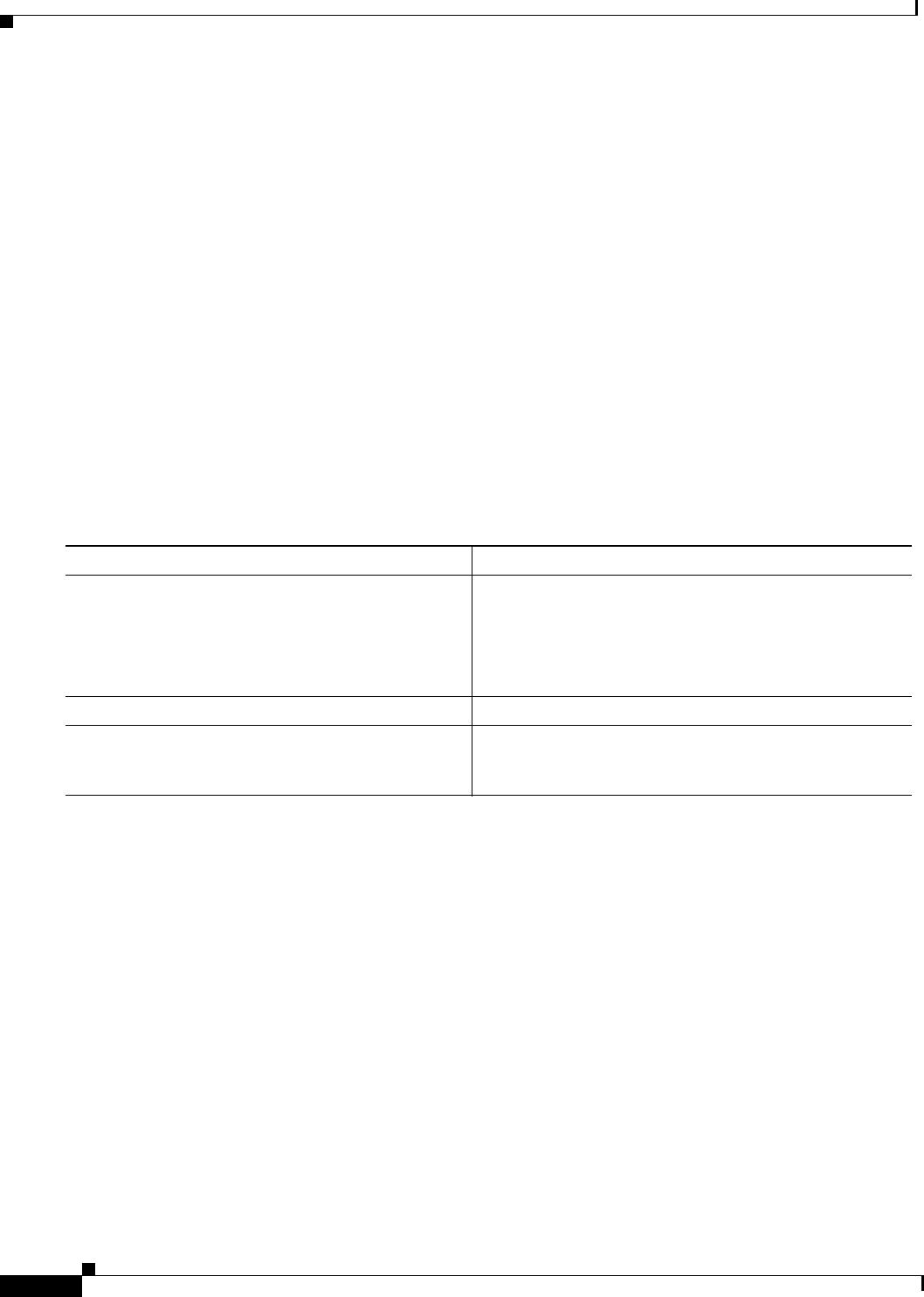
Command Purpose
Step 1
Router(config)# access-list access-list-number
{deny | permit} source [source-wildcard]
Creates a standard access list, repeating the command as
many times as necessary.
Note An access-list entry that uses the deny keyword
creates a multicast boundary for packets that match
that entry.
Step 2
Router(config)# interface type number
Configures an interface.
Step 3
Router(config-if)# ip multicast boundary
access-list [filter-autorp]
Configures the boundary, specifying the access list you
created in Step 1. Optionally configures Auto-RP message
filtering.


















