33
1745D–ATARM–04-Nov-05
AT91M55800A
11.8 Wait States
The EBI can automatically insert wait states. The different types of wait states are listed below:
• Standard wait states
• Data float wait states
• External wait states
• Chip select change wait states
• Early read wait states (as described in Read Protocols)
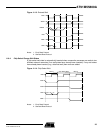
11.8.1 Standard Wait States
Each chip select can be programmed to insert one or more wait states during an access on
the corresponding device. This is done by setting the WSE field in the corresponding
EBI_CSR. The number of cycles to insert is programmed in the NWS field in the same
register.
Below is the correspondence between the number of standard wait states programmed and
the number of cycles during which the NWE pulse is held low:
0 wait states 1/2 cycle
1 wait state 1 cycle
For each additional wait state programmed, an additional cycle is added.
Figure 11-11. One Wait State Access
Notes: 1. Early Read Protocol
2. Standard Read Protocol
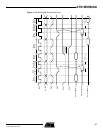
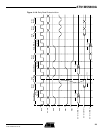
11.8.2 Data Float Wait State
Some memory devices are slow to release the external bus. For such devices it is necessary
to add wait states (data float waits) after a read access before starting a write access or a read
access to a different external memory.
The Data Float Output Time (t
DF
) for each external memory device is programmed in the TDF
field of the EBI_CSR register for the corresponding chip select. The value (0 - 7 clock cycles)
ADDR
NCS
NWE
MCK
1 Wait State Access
NRD
(1)
(2)