264
SX-200 ICP MX Technician’s Handbook
Signaling Types
Channel Associated Signaling
T1 was originally designed to emulate 24 independent analog trunks. The
Channel Associated signaling supports Loop Start, Ground Start, DID/
Loop, and E&M trunks. The function of each channel is decided and
programmed at each end.
All handshake signaling is done with bits (A&B) taken from the bit stream
which are used to emulate the various analog trunk signals, (off-hook,
on-hook, current reversal, etc.).
Common Channel Signaling
The Handshake signaling for the first 23 channels is managed by the 24th
channel. The Common Channel signaling allows for transmission of digital
information and more advanced digital trunk applications (MITEL’s MSDN,
Bell Canada’s Megalink, ISDN, etc.). Signaling protocol is defined by the
type of service.
Test/Verify (T1)
Synchronization
Most T1 issues are a result of connectivity problems.
- Verify that the incoming T1 signal is seen at both ends; verify all
hardware connections. Failure at either end indicates loss of an
incoming synchronizing signal.
- For T1 cards in peripheral cabinets, verify that the switch settings on
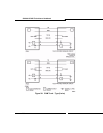
the card are set for proper operation. For example: 1 is closed and 2-8
are open. The S1 Switch Settings for the T1 Trunk Cable Length (not
loop length) are as follows:
0-45.8 m (0-150 ft.): 1only closed (see figure below)
45.8 - 137.3 m (150 - 450 ft.): 2, 3, 4 closed
137.3 - 200.5 m (450 - 655 ft.): 5, 6, 7 closed