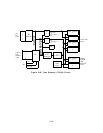
Error Logger:
Prioritizes and stores system errors.
The errors are stored in three error
records (located in System RAM), that are:
●
Permanent System Alarms
● Transient System Errors
● Most Recent System Errors.
The Error Logger lights the Alarm LED (located on the Attendant Console) when a serious
error is detected.
Operating System (OS): Controls all message and data flow to/from the Memory Circuit
Pack, the Arch Angel Driver Interface, to the microprocessors on the port circuit packs, and
to the RS-232 driver interfaces. Messages destined for a particular task are queued until the
associated task can receive them.
When a task has completed a particular process, the next
message is obtained from the message queue of the tasks.
The OS provides an interval timer
that is used to time tasks.
Processes that exceed the set interval (about 60 seconds) are
terminated by the OS.
Arch Angel Driver Interface:
Provides an interface between the OS and Network
Control.
RS-232 Driver Interface: Handles the flow of information between the Call Processor
Circuit Pack and the peripheral equipment of the system (i.e., System Administration
Terminator Advanced Administration PC, Digital Tape Unit, and SMDR Output Device.)
TDM B
US
Provides an electronic link between the system port circuits (including System Resources)
and between the Call Processor Circuit Pack and port circuits.
Port Circuit Packs
Each port circuit pack has on-board software that provides for the sending/receiving of
Network Control messages and data.
Circuit pack status messages are also sent to the
Network Control software.
Step-By-Step Call Description
The following is a description of a call originated between two multilane voice terminals.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
A microprocessor on
a station port circuit pack (port controller) continually
monitors associated port circuits for switchhook status/change and button presses.
When a user goes off-hook, the port controller detects the change.
The port controller
sends an off-hook up-link message along with port
identification to the Call Processor Network Controller (CPNC) via the TDM bus.
The CPNC accepts the message and forwards it to the Operating System (OS) via
the Arch Angel Driver Interface.
The OS checks a message directory to determine which task (i.e., software module)
is to receive the message.
A function of the OS referred to as the “transformer”,
determines it has a message for the Station Call Processing task and queues the
message in RAM.
3-47