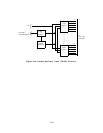
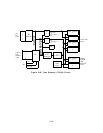
Common Circuitry: The Pooled Modem common circuitry that includes all circuitry shown
on Figure 3-21 except the Conversion Resource circuitry provides the same general function
as the intelligent port common circuitry.
Conversion Resources: The two conversion resources (port circuits) are identical and
each contain the following:
● Microprocessor
● Transmit and Receive I-channel Controller (TRIC)
● Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver and Transmitter (USART)
● Data USART Clock (DUCK)
● Digital Signal Processor (DSP).
The microprocessor controls an on-board data module and modem. This microprocessor
communicates with the port circuit microprocessor over a serial control channel. This
channel allows the on-board microprocessor to send messages to the port circuit
microprocessor specifying call startup information,
option settings, information requests,
various test modes, and call termination information.
It also allows the port circuit
microprocessor
to inform the on-board microprocessor of various port circuit status
information.
The DUCK and TRIC interface I-channel information between the port circuit and the
remote data module. The microprocessor controls the operation of the DUCK and the TRIC
by programming their internal registers. The DUCK and TRIC together recreate the clock
and serial data stream from the remote data module, and process an on-board clock and
serial data stream for delivery to the remote data module.
Control information,
handshaking, and RS-232 control leads is passed between the port circuit microprocessor and
the remote data module by the TRIC.
The USART interfaces the serial data stream of the DUCK to the conversion microprocessor.
The USART can be programmed by the microprocessor to operate synchronously or
asynchronously.
The USART also does the following tasks for the port circuit
microprocessor:
● Appends start and stop bits to parallel data received from the microprocessor in the
asynchronous mode
● Converts serial data received from the DUCK to parallel data
● Buffers data in both directions
● Detects and generates break characters.
The DSP provides modem emulation. It interfaces the port circuit signal and the remote
modem. The microprocessor directs the DSP to execute one of many programs. The DSP
produces data, carrier detection, and timing information for the port circuit microprocessor.
3-44