INTRODUCTION
1-25
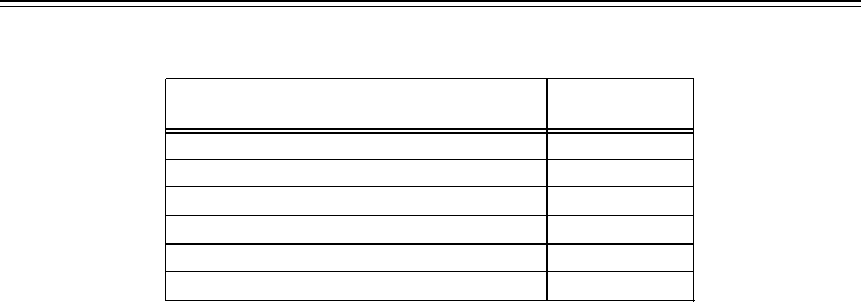
TABLE 1-3. BCCOS
Switch Parameter
Default Value
Analog Lines
0
All trunks except Host Access
0
AAR/ARS Preferences 0
Host Access trunks
1
DCP data modules (both lines and trunks)
1
BRI extensions 0
NOTE: Extensions with multiple appearances must have the
same BC administered for each appearance.
ISDN Call Processing
ISDN-PRI is a trunk signaling type. ISDN trunk signaling is applied on a per-trunk-group basis and
is compatible with most existing switch features. ISDN trunk signaling also supports many new
networking features as described next.
Outgoing Calls
For outgoing calls, ISDN trunk groups may be categorized as those that:
1.
2.
3.
Require that address digits be collected before trunk seizure (this can be done on non-ISDN
trunks)
Seize the trunk and do not outpulse any digits (this is called digit sending)
Seize the trunk, obtain a start dial signal, and then begin digit outpulsing (this is called cut-
through dialing) to the terminating switch
The ISDN protocol requires that all dialed digits be collected before trunk seizure so cut-through
dialing cannot be provided for ISDN calls. Since few applications use digit sending, AAR or ARS
software must be used to collect and process dialed digits. If the switch is properly administered and
the numbering-plan data blocks are correct, AAR or ARS software processes dialed digits based on
data within the routing pattern and routing preference combinations resulting in the selection of a
particular service or feature. The routing pattern and routing preference combinations determine
which outgoing trunk group is selected and whether ISDN-PRI trunk signaling is used.
Each call routed to an ISDN signaling trunk group generates a series of Q.931 messages over the D-
channel. For example, the calling party IE of the ISDN-PRI setup message assembles the dialed
digits as ASCII numbers that correspond to the defined numbering-plan format. Also included
within the setup message are the BC requirements, B-channel identification, and network-specific
facilities (NSF). If the requested facilities are not available, either channel negotiation is begun or, if
appropriate, a cause failure code is returned and the call attempt is dropped. Otherwise, the called
switch responds with a call proceeding or alerting message.


















