INTRODUCTION
1-19
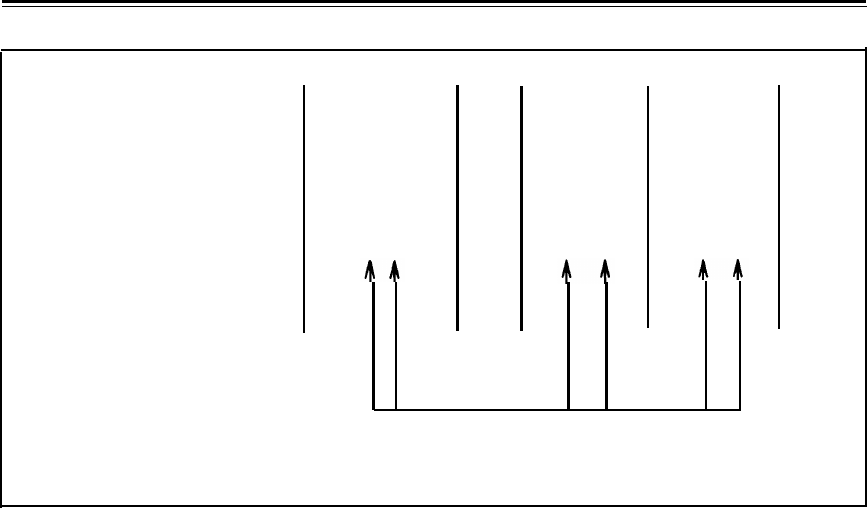
UNCODED
BIT STREAM
010011
00000000
111
00000000 00000000
01
PULSE
STREAM
0+00-+
000+0-+
-+-
000-+0+-
000-+0+-
0+
VIOLATIONS BASED ON POLARITY
OF LAST 1 TRANSMITTED
Figure 1-8. Example of B8ZS Line Coding
Applications requiring B8ZS line coding are currently in the minority, but it is expected that in the
long term they will be in the majority. The B8ZS provides no substantial advantages for voice and
voice-grade data signals over ZCS. However, if the data communications protocol does not already
maintain proper 1s-density, then B8ZS is essential for transmitting unrestricted digital data. Even if
the AT&T network contains unrestricted facilities, the access facilities through the local exchange
may not, which means that you would still be required to use the ZCS option.
Differences Between ZCS and B8ZS
Differences between ZCS and B8ZS include:
1.
2.
3.
4.
ZCS requires that user data be presented via a data communications protocol that does not
generate the all-0s octet, while B8ZS has no such restrictions
ZCS monitors each B-channel (not including the framing bits), while B8ZS monitors the entire
DS1 facility (including framing bits)
ZCS maintains 1s-density at the expense of altering the data, while B8ZS maintains 1s-density
without altering the data
When detecting the all-0s octet with ZCS, the transmit side inserts a 1 in the second LSB,
which will not be corrected from by the receiving side. When detecting eight consecutive 0
S
with B8ZS, switch in the special B8ZS code word. The receive end monitors the DS1 bit
stream and will switch in eight 0s when detecting B8ZS code words.


















