B-8
SAMPLE INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE PROBLEMS
----
SYSTEM 75/SYSTEM 85 OPTIONS:
●
D4 FRAMING
●
PER-CHANNEL SIGNALING
●
ROBBED-BIT SIGNALING
●
ZCS
D4-CHANNEL BANK OPTIONS:
●
D4 FRAMING
●
PER-CHANNEL SIGNALING
●
ROBBED-BIT SIGNALING
●
ZCS
DS1 OR DMI
INTERFACE
TRANSMISSION FACILITY
D4
CHANNEL
BANK
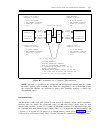
Figure B-8. System 75/System 85 to a D4-Channel Bank
Channels 1 through 24 may be used for almost any combination of trunks. Trunk compatibility is
ensured by translating each channel to match the channel unit installed in the D4.
All trunks are translated in pairs, and the D4 must be equipped accordingly.
It is not advisable to use the spare slots in a channel bank for the storage of unused channel units.
SYNCHRONIZATION-RELATED PROBLEMS
Digital networking with customer-premises digital switches has placed new requirements for planning
and evacuation on the network designer and installer. Each digital switch must now be synchronized
to every other digital switch, digital CO (when applicable), and other DS1 transmission equipment.
The NEC or REC should be involved in planning the network and at the same time come up with a
network synchronization plan.
Synchronization is coordinated timing. A System 75 or System 85 digital switch and other DS1
transmission products all contain an internal timing source. The timing (clock) source conforms to
standards of accuracy that place the clock in a category of accuracy (timing hierarchy). The lower
the number of the stratum clock, the higher the accuracy. Therefore, a system with a stratum-4 clock
would take its timing from a stratum 3 or a stratum 4, a stratum 3 from a stratum 2 or a stratum 3,
and a stratum 2 from a stratum 1 or a stratum 2.
System 75, System 85, CEM, CDM, and D4-channel banks all have internal clocks of stratum-4
accuracy. The most basic rule of synchronization is that timing for all networked products is derived
from the lowest-numbered clock connected (via DS1 facilities) to the device. Synchronization is not
usually a problem when connecting (via DS1 facilities) to a digital CO. Synchronization problems
occur most often in private networks; that is, those networks that do not have any DS1 connections to
equipment outside the private network.