Appendix D Wireless LANs
P-2612HNU-Fx User’s Guide
366
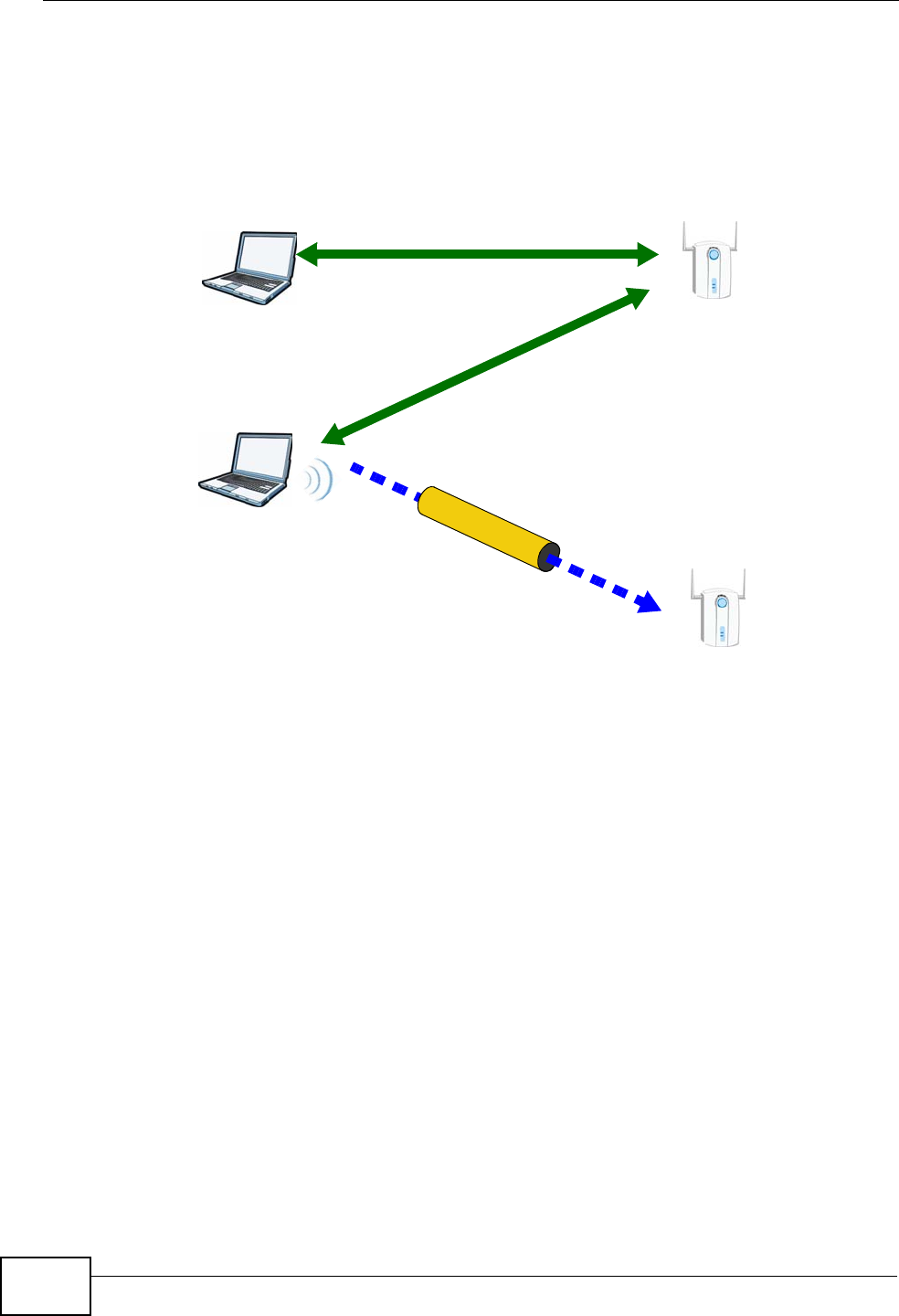
In step 3, you add another access point (AP2) to your network. AP2 is out of
range of AP1, so you cannot use AP1 for the WPS handshake with the new access
point. However, you know that Client 2 supports the registrar function, so you
use it to perform the WPS handshake instead.
Figure 184 WPS: Example Network Step 3
Limitations of WPS
WPS has some limitations of which you should be aware.
• WPS works in Infrastructure networks only (where an AP and a wireless client
communicate). It does not work in Ad-Hoc networks (where there is no AP).
• When you use WPS, it works between two devices only. You cannot enroll
multiple devices simultaneously, you must enroll one after the other.
For instance, if you have two enrollees and one registrar you must set up the
first enrollee (by pressing the WPS button on the registrar and the first enrollee,
for example), then check that it successfully enrolled, then set up the second
device in the same way.
• WPS works only with other WPS-enabled devices. However, you can still add
non-WPS devices to a network you already set up using WPS.
WPS works by automatically issuing a randomly-generated WPA-PSK or WPA2-
PSK pre-shared key from the registrar device to the enrollee devices. Whether
the network uses WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK depends on the device. You can check
the configuration interface of the registrar device to discover the key the
network is using (if the device supports this feature). Then, you can enter the
key into the non-WPS device and join the network as normal (the non-WPS
device must also support WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK).
CLIENT 1
AP1
REGISTRAR
CLIENT 2
EXISTING CONNECTION
S
E
C
U
R
I
T
Y
I
N
F
O
ENROLLEE
AP1
E
X
I
S
T
I
N
G
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
I
O
N