PicoBlaze 8-bit Embedded Microcontroller www.xilinx.com 17
UG129 (v1.1.2) June 24, 2008
R
Chapter 2
PicoBlaze Interface Signals
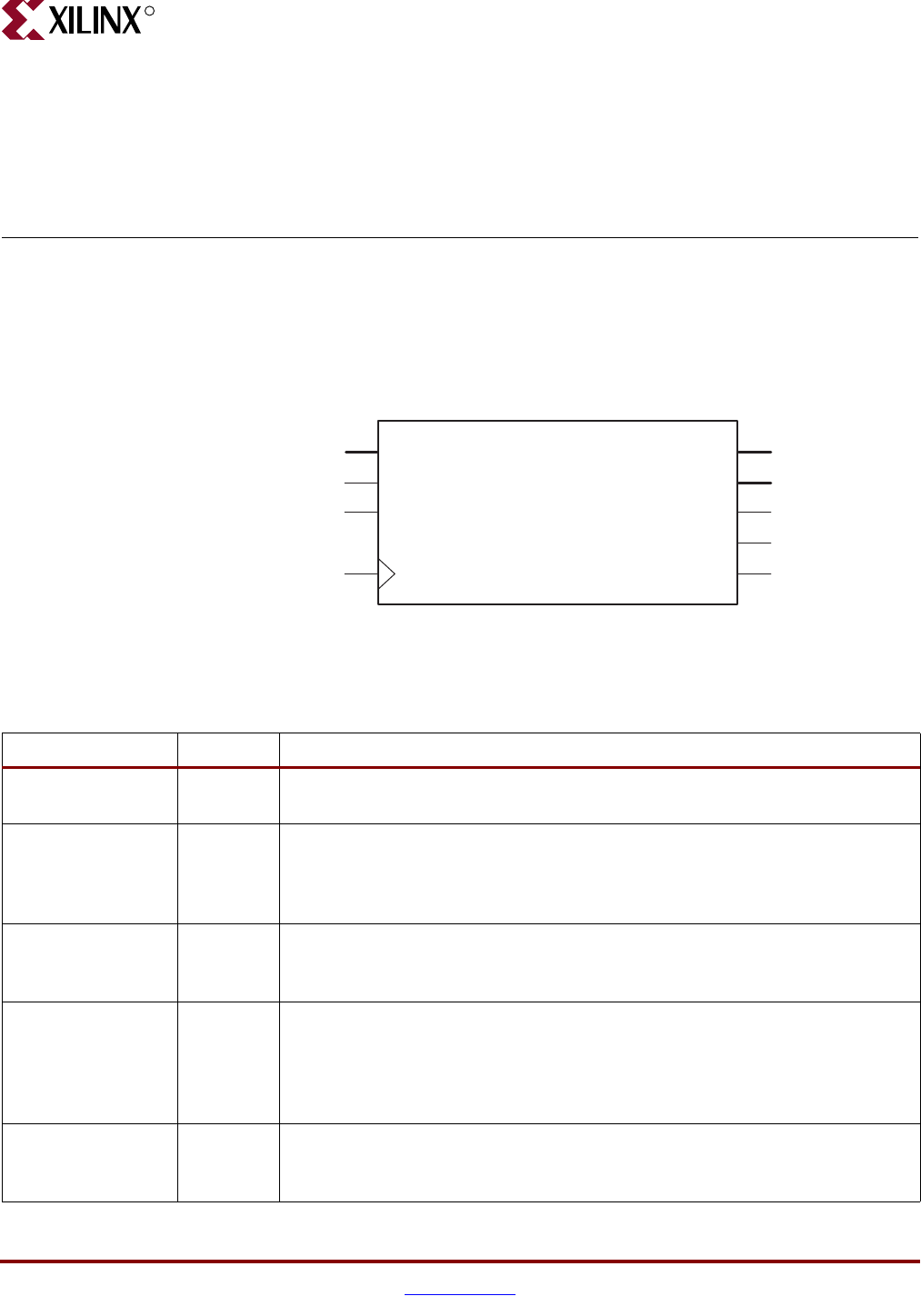
The top-level interface signals to the PicoBlaze™ microcontroller appear in Figure 2-1 and
are described in Table 2-1. Figure 7-1 provides additional detail on the internal structure of
the PicoBlaze controller.
Figure 2-1: PicoBlaze Interface Connections
INTERRUPT_ACK
WRITE_STROBE
READ_STROBE
PORT_ID[7:0]
OUT_PORT[7:0]IN_PORT[7:0]
INTERRUPT
RESET
CLK
PicoBlaze Microcontroller
UG129_c2_01_052004
Table 2-1: PicoBlaze Interface Signal Descriptions
Signal Direction Description
IN_PORT[7:0] Input Input Data Port: Present valid input data on this port during an INPUT
instruction. The data is captured on the rising edge of CLK.
INTERRUPT Input Interrupt Input: If the INTERRUPT_ENABLE flag is set by the application
code, generate an INTERRUPT Event by asserting this input High for at least
two CLK cycles. If the INTERRUPT_ENABLE flag is cleared, this input is
ignored.
RESET Input Reset Input: To reset the PicoBlaze microcontroller and to generate a RESET
Event, assert this input High for at least one CLK cycle. A Reset Event is
automatically generated immediately following FPGA configuration.
CLK Input Clock Input: The frequency may range from DC to the maximum operating
frequency reported by the Xilinx ISE
®
development software. All PicoBlaze
synchronous elements are clocked from the rising clock edge. There are no
clock duty-cycle requirements beyond the minimum pulse width
requirements of the FPGA.
OUT_PORT[7:0] Output Output Data Port: Output data appears on this port for two CLK cycles during
an OUTPUT instruction. Capture output data within the FPGA at the rising
CLK edge when WRITE_STROBE is High.


















