Chapter 17 VPN
EMG5324-D10A User’s Guide
213
• Use ESP security protocol (in either transport or tunnel mode).
•Use IKE keying mode.
• Enable NAT traversal on both IPSec endpoints.
• Set the NAT router to forward UDP port 500 to IPSec router A.
Finally, NAT is compatible with ESP in tunnel mode because integrity checks are performed over the
combination of the "original header plus original payload," which is unchanged by a NAT device. The
compatibility of AH and ESP with NAT in tunnel and transport modes is summarized in the following
table.
Y* - This is supported in the Device if you enable NAT traversal.
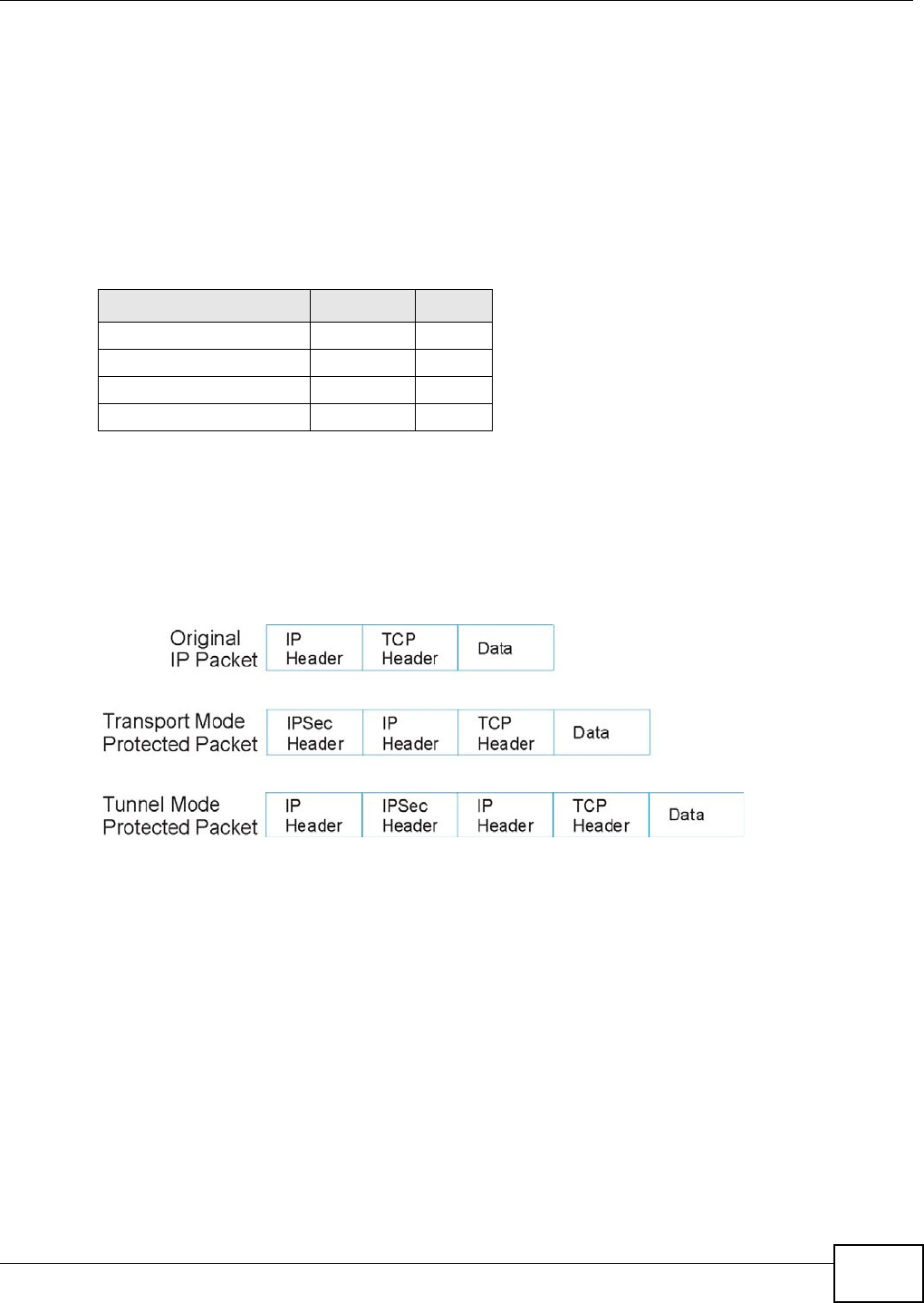
17.6.4 Encapsulation
The two modes of operation for IPSec VPNs are Transport mode and Tunnel mode.
Figure 112 Transport and Tunnel Mode IPSec Encapsulation
Tunnel Mode
Tunnel mode encapsulates the entire IP packet to transmit it securely. A Tunnel mode is required
for gateway services to provide access to internal systems. Tunnel mode is fundamentally an IP
tunnel with authentication and encryption. This is the most common mode of operation. Tunnel
mode is required for gateway to gateway and host to gateway communications. Tunnel mode
communications have two sets of IP headers:
• Outside header: The outside IP header contains the destination IP address of the VPN gateway.
• Inside header: The inside IP header contains the destination IP address of the final system
behind the VPN gateway. The security protocol appears after the outer IP header and before the
inside IP header.
Table 72 VPN and NAT
SECURITY PROTOCOL MODE NAT
AH Transport N
AH Tunnel N
ESP Transport Y*
ESP Tunnel Y


















