Chapter 6 Broadband
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
104
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast packets
go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a specific broadcast
domain.
Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
A tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identify the VLAN membership
of a frame across bridges - they are not confined to the switch on which they were created. The
VLANs can be created statically by hand or dynamically through GVRP. The VLAN ID associates a
frame with a specific VLAN and provides the information that switches need to process the frame
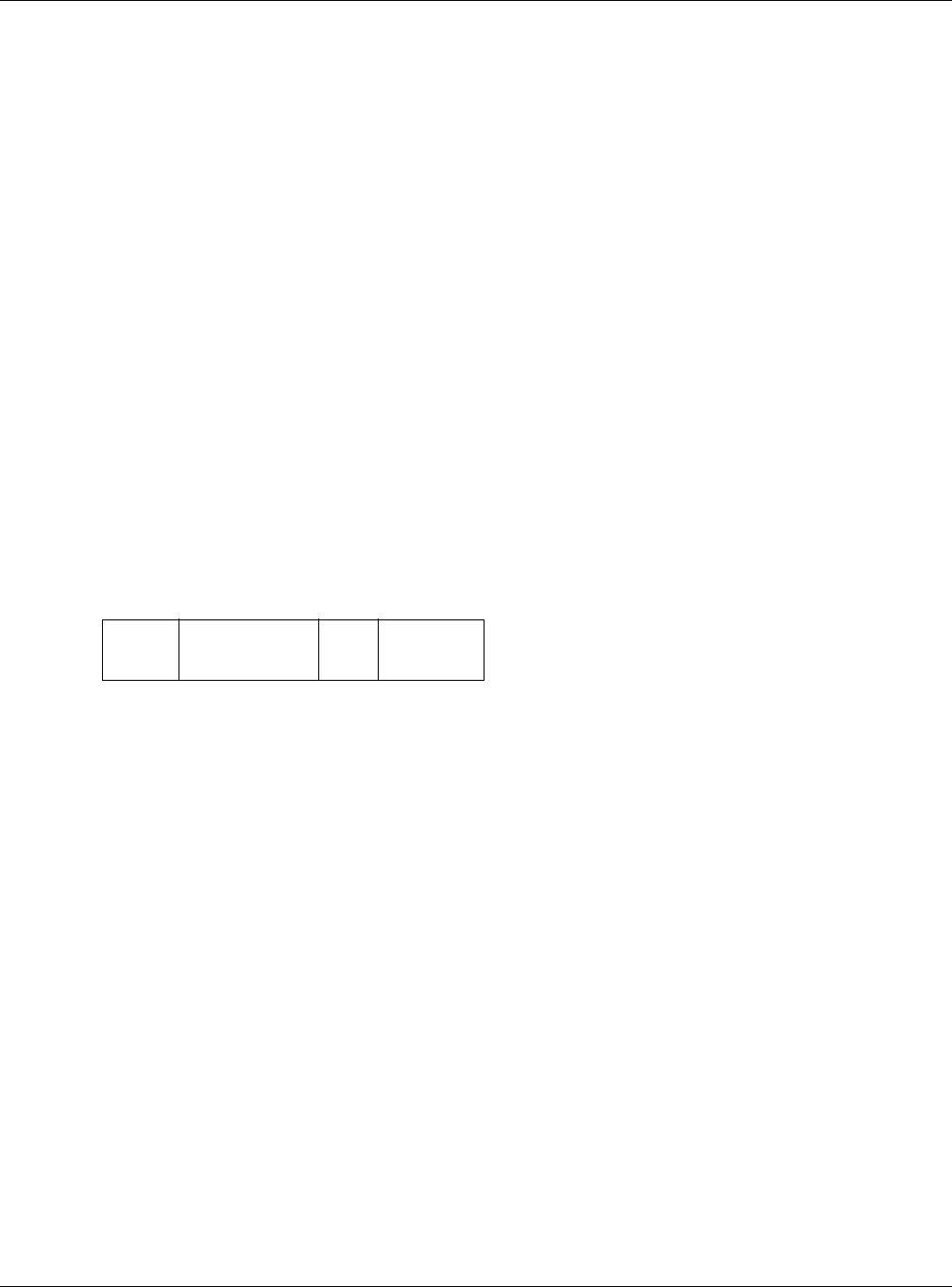
across the network. A tagged frame is four bytes longer than an untagged frame and contains two
bytes of TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier), residing within the type/length field of the Ethernet frame)
and two bytes of TCI (Tag Control Information), starts after the source address field of the Ethernet
frame).
The CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) is a single-bit flag, always set to zero for Ethernet switches. If
a frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not be forwarded as
it is to an untagged port. The remaining twelve bits define the VLAN ID, giving a possible maximum
number of 4,096 VLANs. Note that user priority and VLAN ID are independent of each other. A
frame with VID (VLAN Identifier) of null (0) is called a priority frame, meaning that only the priority
level is significant and the default VID of the ingress port is given as the VID of the frame. Of the
4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is used to identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved,
so the maximum possible VLAN configurations are 4,094.
Multicast
IP packets are transmitted in either one of two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1 recipient) or Broadcast
(1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of hosts on the
network - not everybody and not just 1.
Internet Group Multicast Protocol (IGMP) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership
in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. IGMP version 2 (RFC 2236) is an
improvement over version 1 (RFC 1112) but IGMP version 1 is still in wide use. If you would like to
read more detailed information about interoperability between IGMP version 2 and version 1, please
see sections 4 and 5 of RFC 2236. The class D IP address is used to identify host groups and can be
in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The address 224.0.0.0 is not assigned to any group
and is used by IP multicast computers. The address 224.0.0.1 is used for query messages and is
assigned to the permanent group of all IP hosts (including gateways). All hosts must join the
224.0.0.1 group in order to participate in IGMP. The address 224.0.0.2 is assigned to the multicast
routers group.
At start up, the VMG queries all directly connected networks to gather group membership. After
that, the VMG periodically updates this information.
DNS Server Address Assignment
Use Domain Name System (DNS) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice
versa, for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is extremely
TPID
2 Bytes
User Priority
3 Bits
CFI
1 Bit
VLAN ID
12 Bits


















