– FQDN
Examples
When the filename is not specified, the phone adds {MODEL}.cfg to the end of the URL.
Specified URL Result
– http://10.0.0.2
– http://10.0.0.2/
– http://provisioning.com
– http://provisioning.com/
– http://10.0.0.2/pana
– http://provisioning.com/pana
– http://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://provisioning.com/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://provisioning.com/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://10.0.0.2/pana/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://provisioning.com/pana/{MODEL}.cfg
When the protocol is not specified, the phone adds {MODEL}.cfg to the end of the URL, and also attempts to
contact using all supported protocols.
Specified URL
Result
– 10.0.0.2 – tftp://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
– http://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
– https://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
– ftp://10.0.0.2/{MODEL}.cfg
Note
• If the filename is not defined in the URL, the phone automatically adds the default configuration file
name "{MODEL}.cfg".
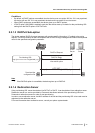
2.2.1 Automatic Discovery of the Provisioning URL
2.2.1.1 SIP PnP
The device sends a SIP SUBSCRIBE message to a multicast IP address (e.g., 224.0.1.75:5060).
Any SIP server in the LAN that listens to that multicast IP address may respond with a valid SIP NOTIFY
message that contains the provisioning URL setting in its body.
Document Version 2014-05 Administrator Guide 37
2.2.1 Automatic Discovery of the Provisioning URL