CHAPTER 2 ND-71762 (E)
Page 8
Issue 2
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR CCIS
4.1 Types of Network
CCIS networks can be divided into the following types, depending upon the numbering plan used:
Main-Satellite Networks
Main-Remote/Campus Networks
Both networks provide uniformity of services throughout the CCIS network, and, because of numbering plan flex-
ibility, station users are not conscious of the distance between nodes.
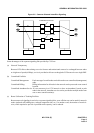
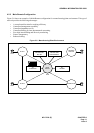
Main/Satellite Network:
In this type of network, offices are connected by means of a numbering plan consisting of a three-digit office code,
which denotes the location, and four-digit station numbers. An example of a Main/Satellite Network is shown in
Figure 2-6.
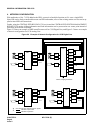
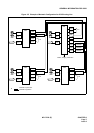
Main-Remote/Campus Network:
In these types of networks, offices are connected by means of a numbering plan consisting of four or five digit station
numbers. The first one or two digit(s) of these station numbers are used to denote the location. An example of a
Main-Campus Network is shown in Figure 2-7. Figure 2-8 shows an example of a Main-Remote Network. In this
network, a part of the Main Office is installed as a Remote Office at a nearby site, either within or outside the pre-
mises of the Main Office. An advantage of this network is that it requires far less cabling than would be necessary
if stations were connected to a single PBX. Network numbering specifications are summarized in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2 Network Specifications
TYPE OF
NETWORK:
MAIN-SATELLITE NETWORK
MAIN-REMOTE/CAMPUS
NETWORK
REMARKS
NUMBERING
PLAN:
Office Code: Three digits
Sta. No.:Four digits
Office Code: First one or two digits of
Station Number.
Sta. No.: Max. five digits
ACCESS
METHOD
8
-XXX-XXXX XXXXX
NETWORK
SIZE:
Large
(Nationwide)
Small (PBX Premises)/
Medium (Local Area)
Sta. No.
Office Code
Access Code
Sta. No.
Office Code