MERLIN LEGEND Communications System Release 6.1
Network Reference
555-661-150
Issue 1
August 1998
Network Management
Page 5-7General Programming in Private Networks
5
source is a Digital Signal 1 (DS1) facility connected to a long-distance carrier
rather than a local exchange carrier. A second choice is a Basic Rate Interface
(BRI) or PRI facility connected to any PSTN carrier. The
Feature Reference
outlines these choices and other alternatives in its “Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
and T1” section.
Clock synchronization derived from the PSTN, either via PRI or BRI facilities, is
always preferable to a clock source that is provided by a digital tandem facility that
is not connected to the PSTN. Private networked systems, however, may not have
an in-service digital PSTN facility available or active. For this reason, clock
synchronization in some private networks requires choosing from among other
clock sources. This is accomplished by programming the clock sources as local
(clock synchronization if provided by a 100D module installed in the local system)
or loop (clock synchronization is provided by a DS1 module installed in a non-
local system). There should be no more than one local clock source for digital
tandem facilities in a private network, and all other tandem facilities are assigned
as loop. A local clock source in a private network is not required; all can be
programmed as loop.
In a private network with three or more systems, it is best if all clock sources for
the private network are on either a hub system (star configuration) or a system
that connects two other switches (series configuration). If the primary clock source
is not functioning, then a secondary or tertiary source on such a system can serve
either all other systems in the private network or two other systems in a private
network. The following examples illustrate how clock synchronization can be
implemented in a private network.
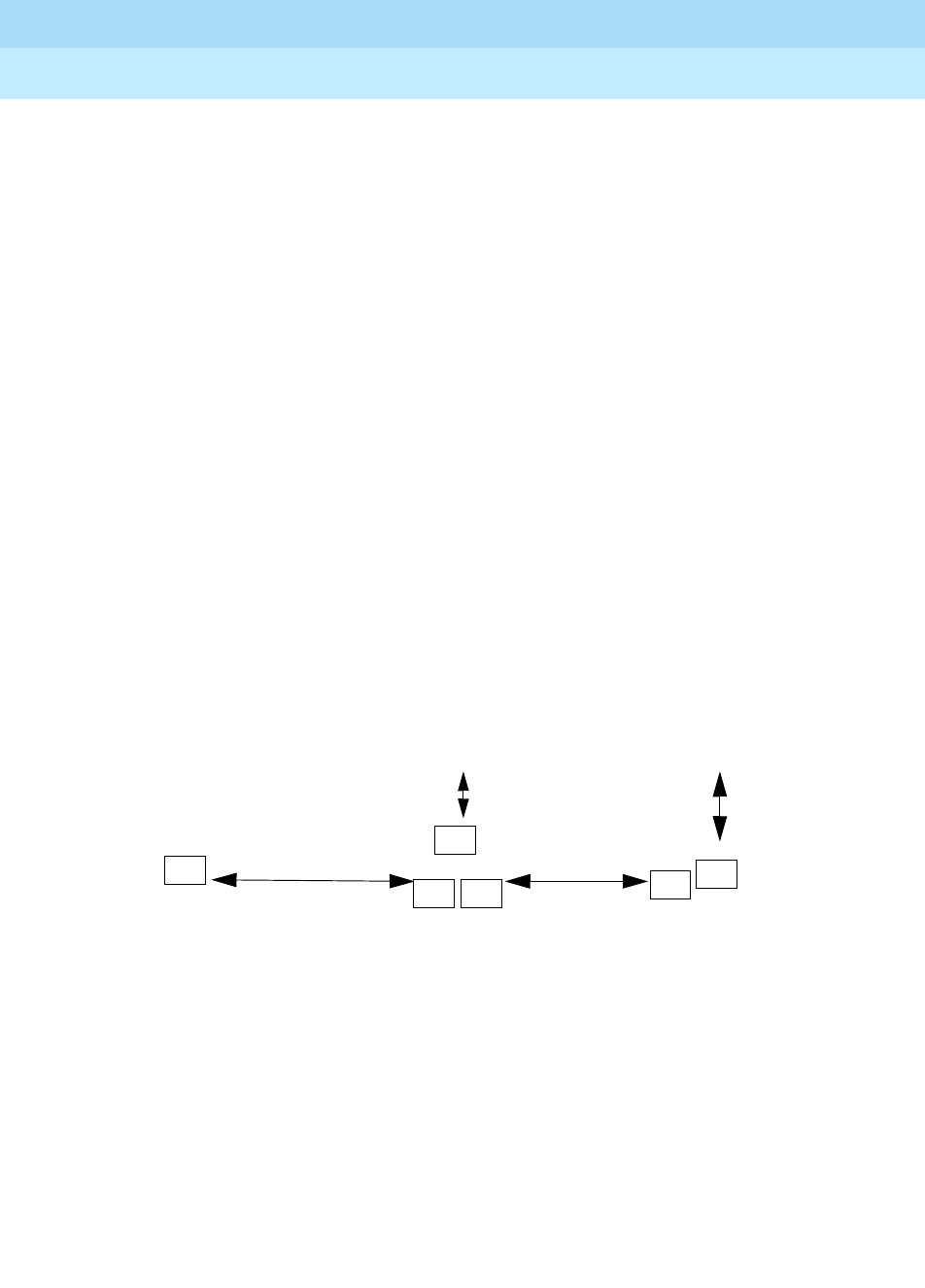
1. If tandem digital facilities link the systems in a private network and a non-
local system is connected to functional digital PSTN facilities, a system
with no digital PSTN facilities assigns its digital tandem lines as loop to
derive the clock source from the system connected at the other end of the
link. Synchronization is derived from the PSTN connection on one private
networked system. The system connecting to the PSTN also assigns its
clock source as loop because its clock source is at the far end of the PSTN
System A
System CSystem B
tandem
PRI
tandem
PRI
100D
100D 100D
100D
100D
PSTN
100D
PSTN
Primary: Loop
Secondary: Local
Tertiary: ______
Primary: PSTN Loop
Secondary: Local C
Tertiary: Local A
Primary: Loop B
Secondary: PSTN Loop
Tertiary: Local B


















