MERLIN LEGEND Communications System Release 6.1
Network Reference
555-661-150
Issue 1
August 1998
Call-Handling Scenarios
Page 2-44Network Configuration Scenarios
2
■ Operator/Receptionist. Each operators/receptionist at headquarters uses
an MLX-20L telephone programmed as a Queued Call Console (QCC).
Callers to either location who wish to speak to an operator/receptionist,
rather than to Intuity AUDIX, can press
and are redirected to the QCC at
headquarters.
■ System Manager. The system manager manages both systems. The
system manager accesses the West Coast system by dialing its Remote
Access code, which is included in the non-local dial plan. For security
reasons, she changes her barrier code two or three times a week. The
system manager has an MLX-20L telephone and uses System
Programming and Maintenance (SPM) for the on-site and remote systems.
The system manager has a dedicated modem to ensure immediate access
to the remote system. Her PC is directly connected to the on-site system.
To help with her own assessments of facilities usage, the system manager
uses each system’s MERLIN LEGEND Reporter application. Working
closely with customer service and sales supervisors, she analyzes the
effectiveness of the system’s facilities during peak and off-peak incoming
calling periods. She ensures that customer service and order-taking agents
understand how to get the most from the lines/trunks that the company
has. MERLIN LEGEND Reporter helps managers balance staffing, staff
training, and facilities needs to serve customers effectively and efficiently.
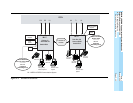
Network Planning 2
In this sample scenario, the two systems are linked in a private network using T1
tandem tie trunks that support fractional point-to-point use. Some channels are
dedicated to voice traffic, emulating analog tie trunks, and some are dedicated to
T1 Switched 56 data.
Figure 2–3
presents some PSTN facilities, types of extensions, and tandem tie
trunks for this company. A few extensions are shown to demonstrate how calls are
handled and how they display for call recipients at different types of extension
equipment. Similarly, sample PSTN facilities are shown in order to illustrate
routing when non-local callers use them or when outside calls are transferred or
routed across the private network.
Non-Local Dial Plans and Facilities Planning 2
This section shows how non-local dial plans, calling groups, switch identifiers,
UDP routing, ARS routing, and remote access are set up for each system. Not all
details are provided for all facilities and extensions.
Table 2–8, page 2-48
shows the applicable extension ranges, patterns, and routes
for pooled facilities when people in one system call people at non-local dial plan
extensions. Pools of T1 Switched 56 channels are reserved for video and data
calls, and intersystem 2B data calls are supported at 112 kbps. At headquarters,
executives conduct videoconferences over PSTN facilities at 128 kbps.