MERLIN LEGEND Communications System Release 6.1
Network Reference
555-661-150
Issue 1
August 1998
Call-Handling Scenarios
Page 2-46Network Configuration Scenarios
2
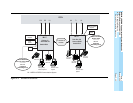
Table 2–9, page 2-49 shows how the system manager sets up the systems so that
users on each system can access the PSTN facilities connected to the other
system. Routing details are summarized in Table 2–10, page 2-50
. As you review
these tables, keep the following points in mind:
■ SMDR is set up to record incoming and outgoing calls with Talk Time
enabled, and MERLIN LEGEND Reporter supplies more refined and
detailed information about the calling group calls on System C, where
order-takers and customer service are located. The system manager must
take time zone differences into account. For example, if an ARS call is
routed over private trunks from System C to System D, System C’s SMDR
report might show the outgoing call, at 2:00 p.m. local time, on a tandem tie
trunk. The same call is reported on System D’s SMDR report at about
12:00 noon local time.
■ In this scenario, UDP routes are set for either voice or data but never both.
Tandem T1 tie trunks do not allocate voice and high-speed data service
dynamically. Because video and 2B data traffic is limited to a few
extensions on each system, most T1 tandem tie channels are used for
voice communications and set for Tie-PBX operation; data tie channels are
programmed for data.
■ Security considerations are paramount because of the seasonal workers
employed both at the headquarters office and the West coast office during
busy sales and shipping periods (although West coast temporary shipping
personnel have less access to telephones). Many extension FRLs are set
to 0 and 1, the most restrictive values. As an extra safeguard, the remote
access default COR FRL is set at 3 on both systems. This allows certain
local ARS routes to be reserved for special purposes and prevents
international calling via a non-local system. As in Scenario 1, barrier codes
are required for non-network and intersystem remote access calls made by
dialing a non-local Remote Access code.
■ The system manager and one technician use the Remote Access codes
programmed into the non-local dial plan to program the other system on
the private network. Therefore the UDP route is set to 6, and only a few
users can access it. The manager and technician use all 11 characters of
their barrier codes and change them two or three times a week.