CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4-8
November 1999
Part No. 001-7780-500
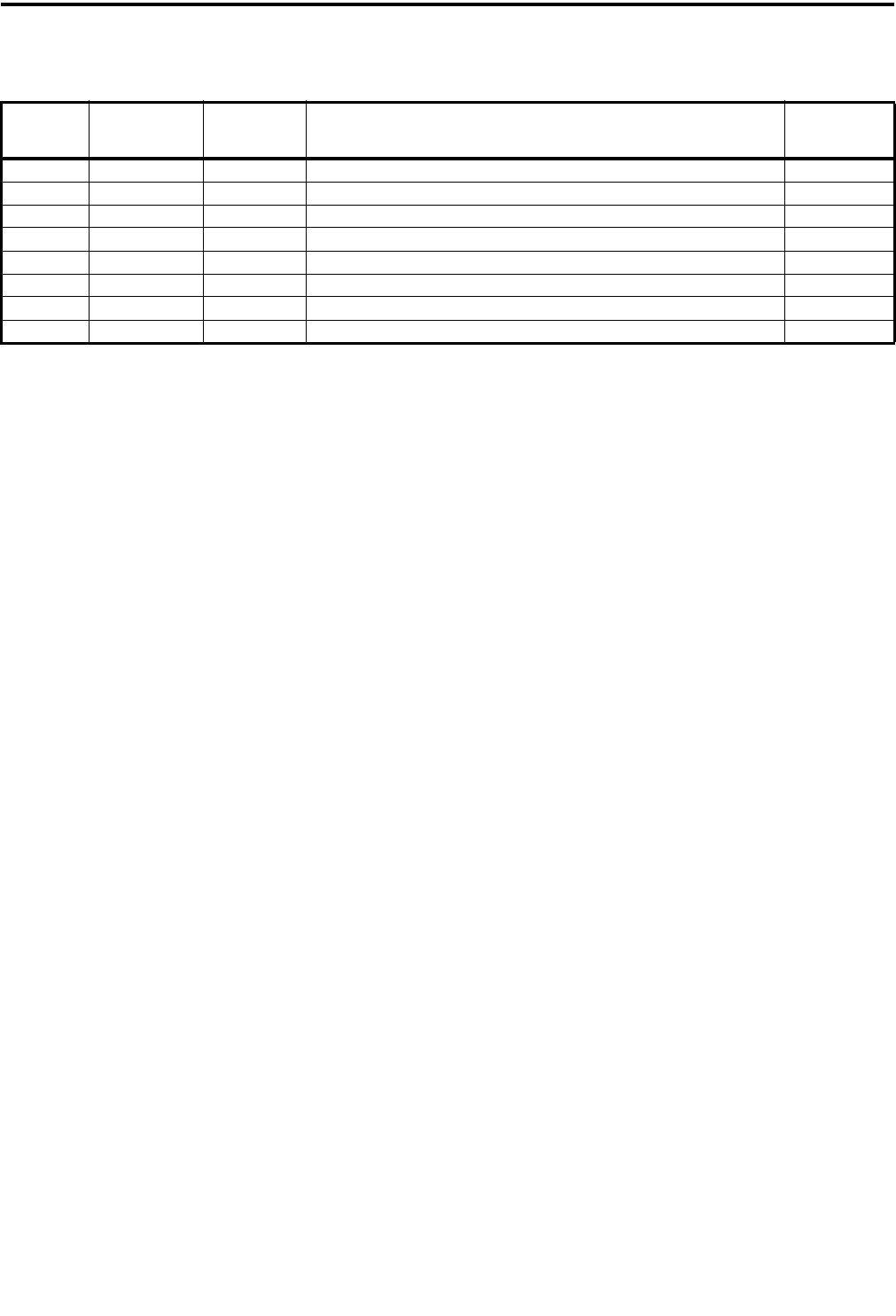
93 S5C Output RF 5C supply control signal High
94 - - - -
95 SN_TR Output SMARTNET circuit control signal (H=SMARTNET Tx Data) High
96 EEPCS Output EEPROM chip select signal -
97 XTXD Output Programming data out -
98 XRXD Input Programming data in -
99 PTTIN Input PTT switch Low
100 - - - -
Table 4-1 Microprocessor IC306 Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin
Name
Port Name
Input or
Output
Description
Active High
or Low
4.6.2 EXPANDER (IC208)
From this filter the signal is fed to pin 7 of the
expander in IC208. When companding is enabled by a
low input on the PT input of IC208, this stage provides
1:2 expansion of the audio signal to remove the 2:1
compression that occurred when it was transmitted.
This compression and then expansion reduces the
amount of noise present in the audio signal. When the
PT input is high, companding is disabled and the
signal if fed through IC208 without expansion. NOTE:
Companding is not currently used with this radio.
The audio signal is fed out of IC208 on pin 15
and then fed to audio mute gate IC103. This gate is
controlled by the RMUTE output (pin 84) of the
microprocessor. The audio is also muted by the audio
amplifier as described in the information which
follows.
4.6.3 AUDIO AMPLIFIER (IC104-IC106)
From gate IC103, the audio signal is fed to
volume control R117 which sets the input level to the
audio amplifiers. Also applied at this point are the
DTMF and beep tones. Muting of the DTMF tones is
provided by Q101 which is controlled by the
DTMFMT output (pin 82) of the microprocessor. The
beep tones are synthesized by the BEEP output (pin
53) of the microprocessor.
The input level to the audio amplifiers is also
controlled by Q112 which lowers the input level by
grounding R168. Both the NPSPAC and W/B (wide/
narrow band) lines control Q112. Resistor R168 is
grounded only in the narrow band/non-NPSPAC mode
(see preceding information for line levels).
With normal operation when the internal speaker
is used, IC105 and IC106 provide the required amplifi-
cation. However, when an external speaker-micro-
phone is connected to pin 1 of the accessory jack (a
load of approximately 1k ohm or less), Q102 and
Q105 turn on and Q109 turns off. This disables IC105
and IC106, and enables IC104.
The supply voltage to all three audio amplifier
stages is controlled by Q106 and Q107. When the
audio is muted such as when no tones are sounding or
no message is being received, the AMUT output of the
microprocessor (pin 85) is low. This turns off both
Q106 and Q107 and removes supply voltage from the
audio amplifiers. This helps conserve battery power.
The receive audio signal is also muted by gate IC103
as previously described.
4.7 RECEIVE AND TRANSMIT DATA
PROCESSING
4.7.1 RECEIVE DATA FILTER/DETECTOR
(IC102A/B, IC107A/B)
The receive data (and audio) signal (DET) from
the IF board is also routed to the receive data filter
formed by IC102B and IC102A. This is a low-pass
filter which attenuates voice and other harmonic
frequencies above the data band.
The passband of this filter is controlled by the
BWC signal applied to Q103. When digital Call Guard
data or a low-frequency Call Guard tone is being
detected, the BWC signal is high which turns on
Q103. The cut-off frequency of the filter is then
approximately 150 Hz. Then when a high-frequency
Call Guard tone is received, Q103 turns off and the


















