311
Clipping Clipping occurs when a signal level exceeds the maximum level a circuit can handle. This is usually
caused by improper gain settings. Clipping causes distortion, listener fatigue, and accelerated failure of speakers.
Compression An induced reduction in the dynamic range of all or part of an audio signal. Compression is usually
used to protect individual loudspeaker components from damage caused by transient peaks in audio signals.
Compressor A signal processor used to perform compression and control the dynamic range of an audio signal.
Control Bus Part of the Expansion Bus, the Control Bus passes control information to the units. Control is not
affected by audio master/slave settings and will continue to function even if the units are not using the audio
channels. See also Expansion Bus.
Crossover A device that passes designated frequency ranges of an audio signal to specified loudspeaker
elements in a sound system. Converge Pro provides the following types of crossovers:
Bessel• A crossover using a low-pass filter design characterized by a linear phase response. This results in a
constant time delay throughout the passband.
Butterworth• A crossover using a low-pass filter design characterized by a maximally flat magnitude
response. This results in no amplitude ripple in the passband.
Linkwitz-Riley• A fourth-order crossover consisting of a cascaded second order Butterworth low-pass filter.
Offers a vast improvement over the Butterworth crossover and is the de facto standard for professional audio
active crossovers.
Cross Point The intersection between an input and an output in the routing matrix. Cross point cells are color
coded according to input type: yellow = gated; blue = non-gated; brown = pre-AEC; green = cross point. See also
Gating, Pre-AEC Channel.
Cross Point Level Adjust The process of adjusting the audio level (gain/attenuation) at the cross point. Cross
Point Levels are set using the Cross Point Attenuation Slider, which allows you attenuate the signal from 0 to -60dB
(it also allows you to add gain to the signal, from 0 to 12dB).
Decay Rate Determines how fast a mic input channel gates off after the specified Hold time expires (slow, medium,
fast). The default is medium.
Default Meter The input/output level meter displayed on the front panel LED meter. All Converge Pro meters are
peak-level meters.
Delay Delay calculates the amount of signal delay based on the distance between audio source and audience, and
the temperature. Introducing an appropriate amount of delay can maintain acoustical alignment and proper sound
imaging in a room regardless of speaker location. This setting can also compensate for propagation delay caused
by signal processing, such as analog to digital conversion. Delay is set in the Channel Property Configuration
window for Processing channels. See also Processing Blocks.
Device ID A number which identifies the unit when multiple units of the same device type are connected via the
Expansion Bus. All Converge Pro units ship from the factory with a default DID of 0.
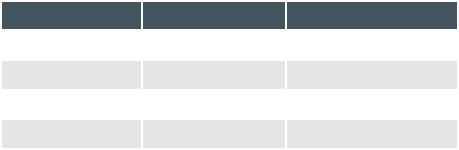
Device Type A number which identifies the type of unit. Converge Pro Device Types and Device IDs by model are
as follows:
Model Device Type Device ID Range
880 1 0-7
TH20 2 0-F
840T 3 0-7
8i A 0-7
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Part of the IP protocol suite, DHCP enables a host server to
dynamically assign IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other parameters to devices on IP-based
networks. See also Default Gateway and Subnet Mask.


















