Appendix F NAT
P-2304R-P1 Series User’s Guide
263
The following table summarizes how these NAT types handle outgoing and incoming packets.
Read the following sections for more details and examples.
The examples in these NAT type sections describe NAT translation between internal (private)
and external (public) IP addresses.
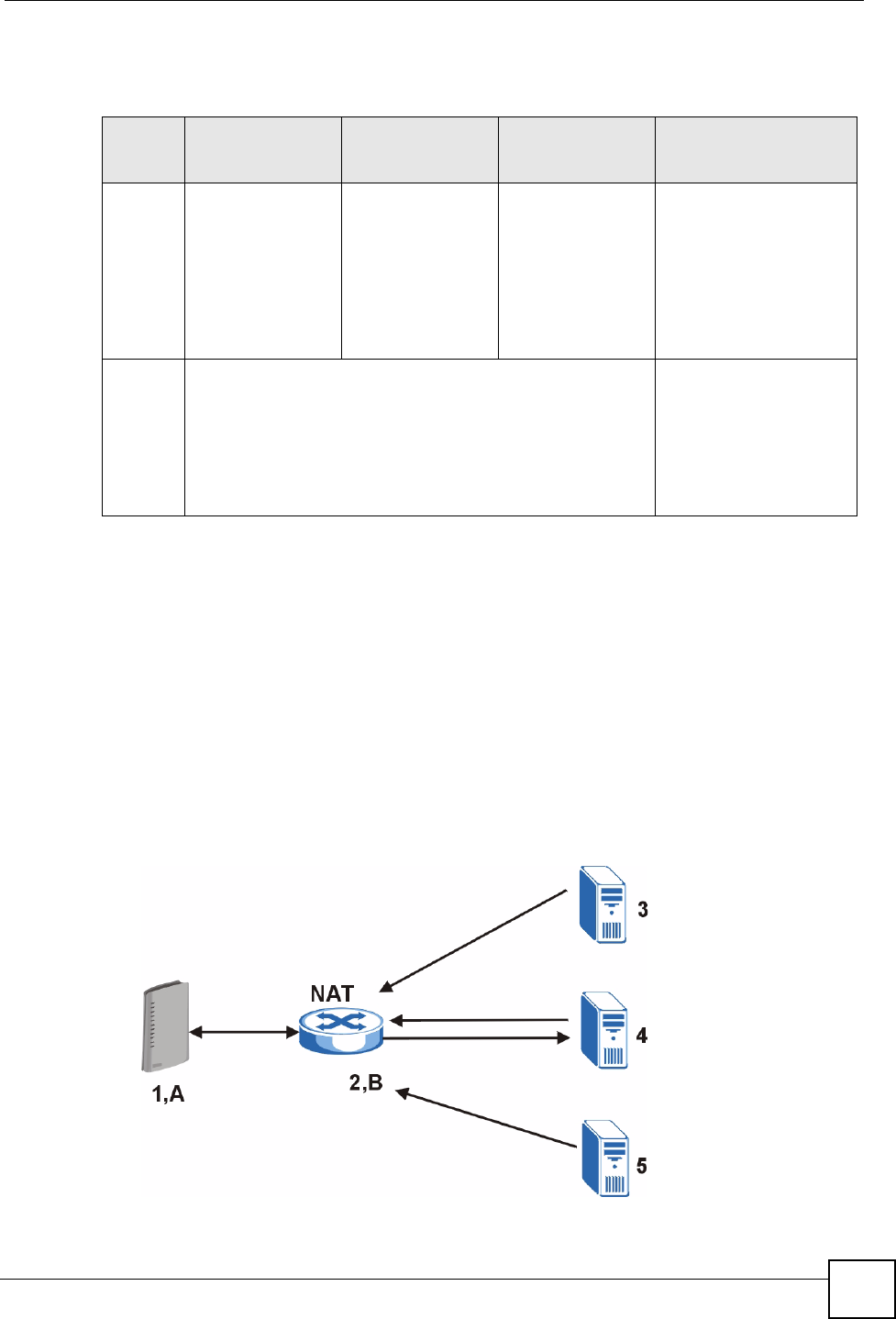
Full Cone NAT
In full cone NAT, the NAT router maps all outgoing packets from an internal IP address and
port to a single IP address and port on the external network. The NAT router also maps
packets coming to that external IP address and port to the internal IP address and port.
In the following example, the NAT router maps the source address of all packets sent from the
ZyXEL Device’s internal IP address 1 and port A to IP address 2 and port B on the external
network. The NAT router also performs NAT on all incoming packets sent to IP address 2 and
port B and sends them to IP address 1, port A.
Figure 155 Full Cone NAT Example
Table 127 NAT Types
FULL CONE
RESTRICTED
CONE
PORT
RESTRICTED
CONE
SYMMETRIC
Incoming
Packets
Any external host
can send packets
to the mapped
external IP address
and port.
Only external hosts
with an IP address
to which the
internal host has
already sent a
packet can send
packets to the
mapped external IP
address and port.
Only external hosts
with an IP address
and port to which
the internal host
has already sent a
packet can send
packets to the
mapped external IP
address and port.
A host on the external
network can only send
packets to the specific
mapped external IP
address and port that the
NAT router used in
sending a packet to the
external host’s IP
address and port.
Outgoing
Packets
The NAT router maps the internal IP address and port of all
outgoing packets to a single IP address and port on the
external network.
The NAT router maps the
internal IP address and
port of each outgoing
packet to a different
external IP address and
port for each different
destination IP address
and port.


















