RTP
Issue 6 January 2008 331
For each codec, there was an attempt to verify that the audio packets were received intact. This
was done by spot checking the audio packets before and after compression, using two Sniffer
protocol analyzers. For every codec except G.711, the RTP header and payload were identical
before and after compression. With G.711, however, the received packets had the PADDING
flag set in the RTP header, although the flag was not set when the packets were transmitted.
The PADDING flag indicates the presence of padding octets at the end of the RTP payload,
which cannot be true for G.711.
Configuration
To configure RTP header compression on a Cisco router:
1. Specify the number of RTP connections that can be compressed (cache allocation). In
interface configuration mode, the command is ip rtp compression-connections
<number>, where
● The default for <number> is 32, and each call requires two connections.
● The configurable range is 3 to 256 for PPP and HDLC using IOS v11.3 and later.
● The configurable range is 3 to 1000 for PPP and HDLC using IOS v12.0(7)T and later.
● For Frame Relay, the value is fixed at 256.
2. The command to turn on compression is ip rtp header-compression in interface
configuration mode. It must be implemented at both ends of the WAN link. When the
command was entered into the router, ip tcp header-compression was also installed
automatically. When either command was removed, the other was automatically removed.
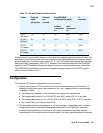
Table 57: Test call (20ms-packets) results
Codec Payload
bytes
per packet
Packets
per
second
Avg WAN BW
consumption (kbps)
%
reduction
without
compressi
on
with
compressi
on
G.711
(64 kbps)
160 50 84 68.5 ~18%
G.729A
(8 kbps)
20 50 27.5 13 ~53%
G.723.1
(5.3 kbps)
20 33 18 9 ~50%
G.723.1
(6.3 kbps)
24 33 19 10 ~47%