Traffic engineering
194 Avaya Application Solutions IP Telephony Deployment Guide
In addition, 37% of intercom calls that are generated in Site 1 are generated by circuit-switched
stations, and 69% of those calls are terminated by IP stations. Since 69% of 37% is 25.5%,
25.5% of Site 1 to Site 2 intercom calls are circuit-switched station to IP station. Finally, 37% of
intercom calls that are generated in Site 1 are generated by circuit-switched stations, and 31%
of those calls are terminated by circuit-switched stations. Since 31% of 37% is 11.5%, 11.5% of
Site 1 to Site 2 intercom calls are circuit-switched station to circuit-switched station.
So, since 43.5% of Site 1 to Site 2 intercom calls are IP station to IP station, Site 1 IP station to
Site 2 IP station CUR is 43.5% of the 12 Erlangs of overall Site 1 to Site 2 intercom CUR, or 5.2
Erlangs. Similarly, the Site 1 IP station to Site 2 circuit-switched station CUR is equal to 19.5%
of 12 Erlangs, or 2.3 Erlangs, and the Site 1 circuit-switched station to Site 2 IP station CUR is
equal to 25.5% of 12 Erlangs, or 3.1 Erlangs. Finally, the Site 1 circuit-switched station to Site 2
circuit-switched station CUR is 11.5% of 12 Erlangs, or 1.4 Erlangs.
The values for the remaining COI cells that correspond to intercom traffic for this example are
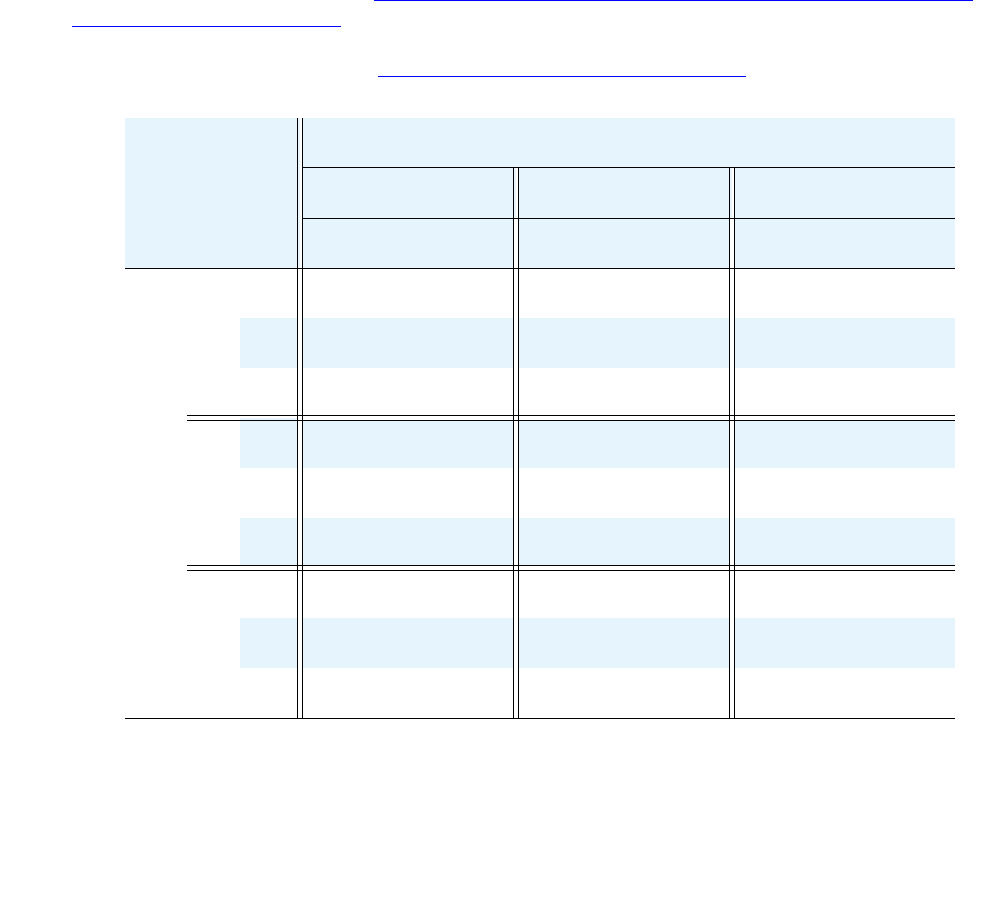
calculated in a similar manner. Table 31:
COI matrix for Example 4: Expanded COI matrices
(intercom CUR values only) summarizes the results of that exercise:
Table 31: COI matrix for Example 4: Expanded COI matrices
(intercom CUR values
only)
To endpoints in site ___
1 2 3
I C P I C P I C P
From endpoints in site ___
1
I
12.7 7.5 5.2 2.3 2.8 0.37
C
7.5 4.4 3.1 1.4 1.6 0.22
P
2
I
5.2 3.1 1.9 0.85 1.2 0.16
C
2.3 1.4 0.85 0.37 0.54 0.07
P
3
I
2.8 1.6 1.2 0.54 0.78 0.10
C
0.37 0.22 0.16 0.07 0.10 0.01
P


















