Migration from DEFINITY Server R to S8700 fiber-PNC
Issue 6 January 2008 123
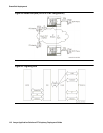
At this stage, the media flow between two IP endpoints can be “shuffled.” That is, the media flow
proceeds directly between both endpoints without requiring Media Processor resources.
Shuffling may be used across multiple sites or multiple Avaya switches. Likewise, calls between
an IP endpoint at one site and a circuit-switched endpoint at another site can be shuffled so that
the media stream flows between the IP Telephone and the Media Processor circuit pack in the
Port Network that is connected to the circuit-switched endpoint. By using the IP network to the
greatest extent possible, enterprises can minimize the use of expensive circuit-switched trunks.
Figure 45: IP-enabling the S8700 fiber-PNC configuration
Phase 3: Server consolidation
Traditionally, some enterprises have elected to use multiple DEFINITY systems at remote sites
to protect against a circuit failure on the center stage network bringing down an entire remote
site. With the decision to run multiple servers came the need for additional administrative
resources and a more complex dial plan. Today, through the use of IP Telephony technology
and the enhanced processing capabilities of the S8700-series Servers, Avaya has a solution to
consolidate smaller remote DEFINITY servers, such as ProLogix or DEFINITY ONE into an
S8700 fiber-PNC system, while maintaining remote site survivability in the event of a network or
processor failure. By consolidating multiple DEFINITY servers into one S8700 system, an
enterprise can realize cost savings in simplified administration and a simplified dial plan. With
support for up to 44,000 endpoints, the S8700-series system has the scalability to support a
remote site’s server consolidation.