12-5
Catalyst 2950 Desktop Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-11380-05
Chapter 12 Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
Understanding Optional Spanning-Tree Features
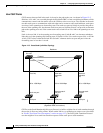
Figure 12-3 UplinkFast Example Before Direct Link Failure
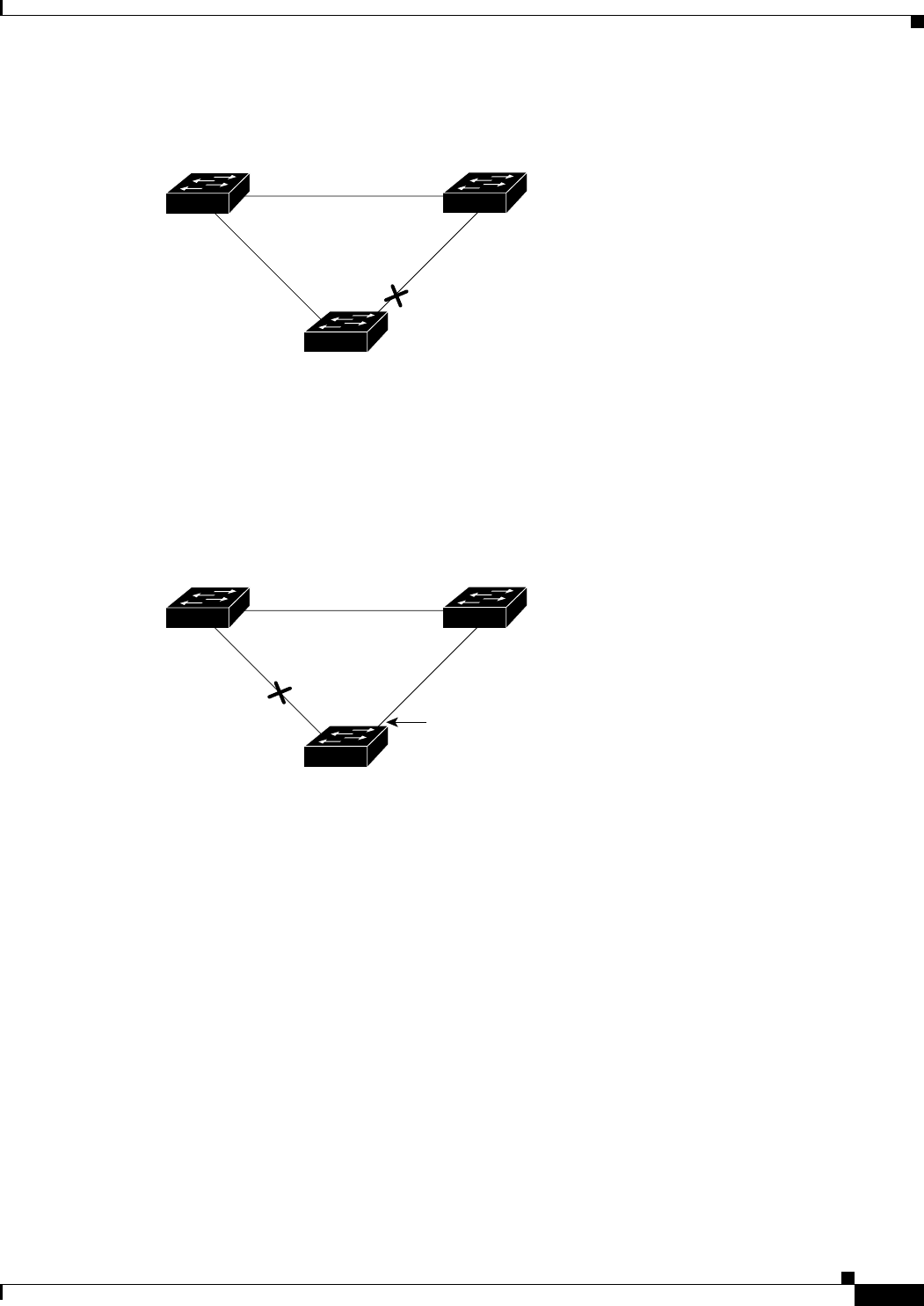
If Switch C detects a link failure on the currently active link L2 on the root port (a direct link failure),
UplinkFast unblocks the blocked port on Switch C and transitions it to the forwarding state without
going through the listening and learning states, as shown in Figure 12-4. This change takes
approximately 1 to 5 seconds.
Figure 12-4 UplinkFast Example After Direct Link Failure
Understanding Cross-Stack UplinkFast
Cross-stack UplinkFast (CSUF) provides a fast spanning-tree transition (fast convergence in less than
1 second under normal network conditions) across a stack of switches that use the GigaStack GBICs
connected in a shared cascaded configuration (multidrop backbone). During the fast transition, an
alternate redundant link on the stack of switches is placed in the forwarding state without causing
temporary spanning-tree loops or loss of connectivity to the backbone. With this feature, you can have
a redundant and resilient network in some configurations. You enable CSUF by using the spanning-tree
stack-port interface configuration command. The CSUF feature is supported only when the switch is
running PVST.
CSUF might not provide a fast transition all the time; in these cases, the normal spanning-tree transition
occurs, completing in 30 to 40 seconds. For more information, see the “Events That Cause Fast
Convergence” section on page 12-7.
L1
L2 L3
Switch C
Switch A
(Root)
Switch B
Blocked port
43575
L1
L2 L3
Switch C
Switch A
(Root)
Switch B
UplinkFast transitions port
directly to forwarding state.
Link failure
43576