Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
V300 User’s Guide
109
10.1.7.1 STUN
STUN (Simple Traversal of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) through Network Address
Translators) allows the V300 to find the presence and types of NAT routers and/or firewalls
between it and the public Internet. STUN also allows the V300 to find the public IP address
that NAT assigned, so the V300 can embed it in the SIP data stream. STUN does not work
with symmetric NAT routers or firewalls. See RFC 3489 for details on STUN.
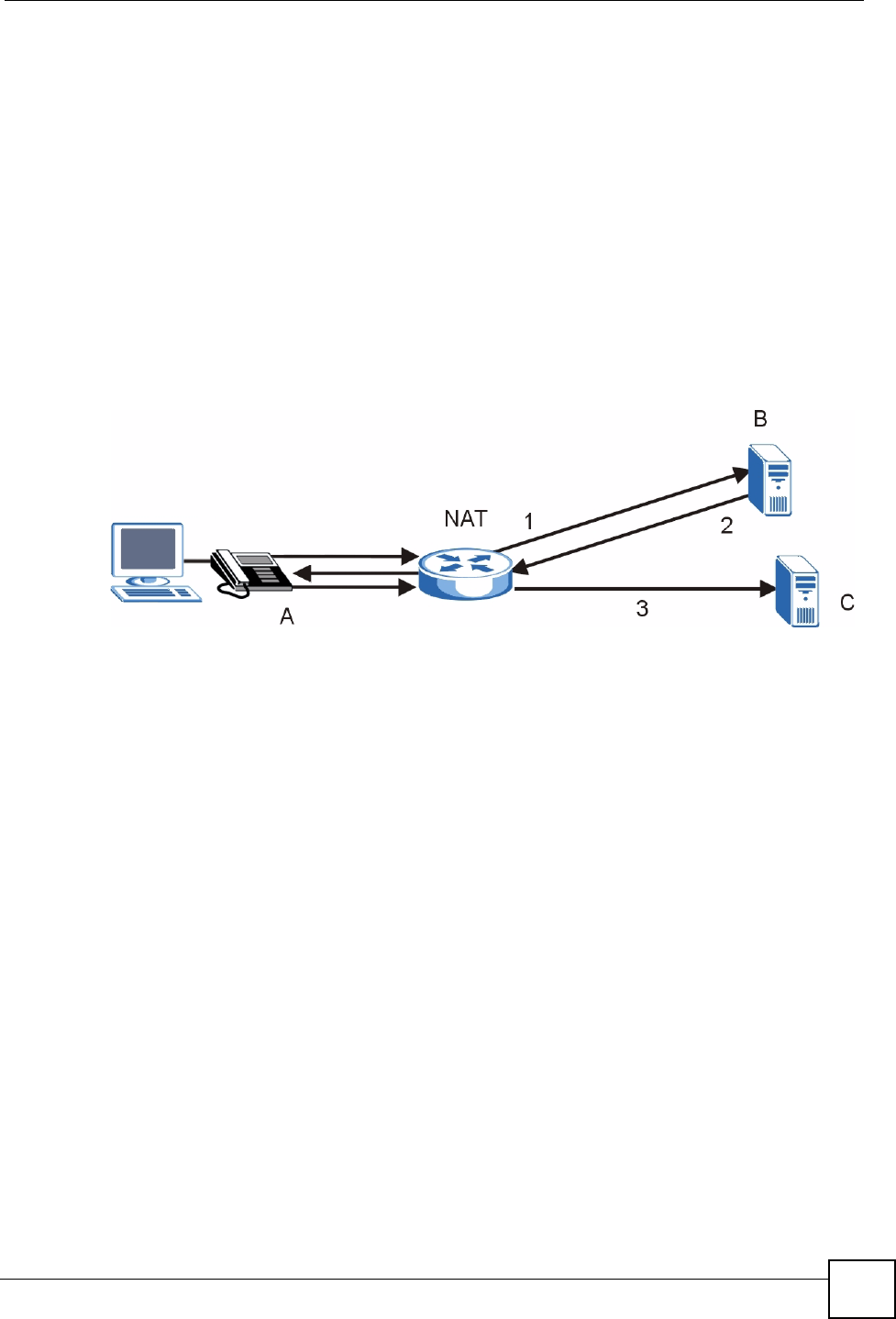
The following figure shows how STUN works.
1 The V300 (A) sends SIP packets to the STUN server (B).
2 The STUN server (B) finds the public IP address and port number that the NAT router
used on the V300’s SIP packets and sends them to the V300.
3 The V300 uses the public IP address and port number in the SIP packets that it sends to
the SIP server (C).
Figure 121 STUN
10.1.7.2 Outbound Proxy
Your VoIP service provider may host a SIP outbound proxy server to handle all of the V300’s
VoIP traffic. This allows the V300 to work with any type of NAT router and eliminates the
need for STUN or a SIP ALG. Turn off a SIP ALG on a NAT router in front of the V300 to
keep it from retranslating the IP address (since this is already handled by the outbound proxy
server).
10.1.8 Voice Coding
A codec (coder/decoder) codes analog voice signals into digital signals and decodes the digital
signals back into voice signals. The V300 supports the following codecs.
• G. 7 11 is a Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) waveform codec. PCM measures analog signal
amplitudes at regular time intervals (sampling) and converts them into digital bits
(quantization). Quantization “reads” the analog signal and then “writes” it to the nearest
digital value. For this reason, a digital sample is usually slightly different from its analog
original (this difference is known as “quantization noise”).
G.711 provides excellent sound quality but requires 64kbps of bandwidth.
• G. 7 2 3 is an Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM) waveform codec.
Differential (or Delta) PCM is similar to PCM, but encodes the audio signal based on the
difference between one sample and a prediction based on previous samples, rather than
encoding the sample’s actual quantized value. Many thousands of samples are taken each
second, and the differences between consecutive samples are usually quite small, so this
saves space and reduces the bandwidth necessary.


















