Overview of Voice over IP (VoIP) and Network Protocols
36 4600 Series IP Telephone LAN Administrator Guide
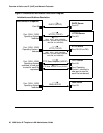
Initialization Process
These steps offer a high-level description of the information exchanged when the telephone
initializes and registers. This description assumes that all equipment is properly administered
ahead of time. This description can help you understand how the 4600 Series IP Telephones
relate to the routers and servers in your network.
Step 1: Telephone to Network
The telephone is appropriately installed and powered. After a short initialization process, the
telephone identifies the LAN speed. If applicable to your network and telephone model, 802.1X
Supplicant authentication occurs at this time, where an 802.1X ID and password have to be
submitted to proceed. Then the telephone sends a DHCP message out into the network,
identifying itself and requesting further information. Depending on your network structure, the
message goes directly to the DHCP server or a network router receives the message and relays
it to the appropriate DHCP server.
Step 2: DHCP Server to Telephone
The DHCP file server provides information to the telephone, as described in DHCP and File
Servers on page 59. Among other data passed to the telephone is the IP address of the TFTP
or HTTP server, which is crucial for the next step.
Step 3: Telephone and File Server
Many 4600 Series IP Telephones can download script files, application files, and settings files
from either a TFTP, HTTP, or HTTPS server. For specific telephone/server compatibility, see
Table 1
. If you have a mixture of telephones, you can use either:
● TFTP servers only.
● Both TFTP and HTTP servers, with TFTP running telephones with older releases and
HTTP for telephones capable of using HTTP.
You need TFTP servers for upgrades if you have a release prior to R2.2 on a telephone.
Currently, only Avaya servers support 4600 Series IP Telephone file transfers using HTTPS.
The reason is 4600 Series IP Telephones only establish encrypted TLS connections with
servers that use Avaya-signed digital certificates.
A telephone that supports HTTP will attempt to access the HTTP server (if administered), and, if
successful, will not attempt to access the TFTP server (if administered).