4600 Series IP Telephone LAN Administrator’s Guide
QoS
4-28
For 4610SW/4620/4620SW/4630/4630SW IP Telephones, the following parameters are displayed
in real-time to users on the appropriate screens, while on a call:
For 4602/4602SW/4606/4612/4624 IP Telephones, the Network Audio Quality Screen presents
the user with a qualitative assessment of the overall audio quality currently being experienced.
This assessment is based on separate evaluations of the Packet Loss and the total Network Delay
(the sum of Packetization Delay, One-way Network Delay, and Network Jitter Compensation
Delay), and consideration of the codec in use. You can disable the display of the Network Audio
Quality data and assessment for all sets by setting the system value NTWKAUDIO to a value of
“0” as explained in Administering Options for the 4600 Series IP Telephones, on page 4-30
.
The implication of this information for LAN administration depends, of course, on the values
reported by the user and the specific nature of your LAN (topology, loading, QoS administration,
etc.). The major use for this information is to give the user an idea of how network conditions are
affecting the audio quality of the current call. It is assumed you have more detailed tools available
for troubleshooting the LAN.
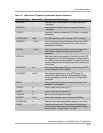
Table 4-4. Parameters in Real-Time
Parameter Possible Values
Audio Connection
Present?
Yes (if a receive RTP stream has been established)
No (if a receive RTP stream has not been established)
Received Audio
Coding
G.711 or G.729
Silence Suppression Yes (if the telephone knows the far-end has silence suppression
Enabled)
No (if the telephone knows the far-end has silence suppression
Disabled, or the telephone does not know either way)
Packet Loss No data or a decimal percentage. Late and out-of-sequence
packets are counted as lost if they are discarded. Packets are not
counted as lost until a subsequent packet is received and the loss
confirmed by the RTP sequence number.
Packetization Delay No data or an integer number of milliseconds. The number reflects
the amount of delay in received audio packets, and includes any
look-ahead delay associated with the codec.
One-way Network
Delay
No data or an integer number of milliseconds. The number is one-
half the value RTCP computes for the round-trip delay.
Network Jitter
Compensation Delay
No data or an integer number of milliseconds reporting the average
delay introduced by the telephone’s jitter buffer.