FDTD codes use periodic boundary conditions. Fields leaving through one side will
magically reappear coming from the other, which may lead to divergences if you don’t
put in absorbers of some sort. Sloppy absorber design may lead to fields travelling many,
many periods, leading to anomalously slow convergence. Figure 2.4 is an example of a
divergence due to PMLs used with plane wave sources. Note that the divergence looks
electrostatic—the wavelength is far too short to propagate. This is a good clue that
something is wrong.
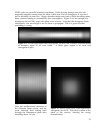
Figure 2.5: 120-µm long doped silica waveguide, excited with a circular Gaussian beam
of diameter equal to its core width. A black glass region is at each end
(waveguide1c.par).
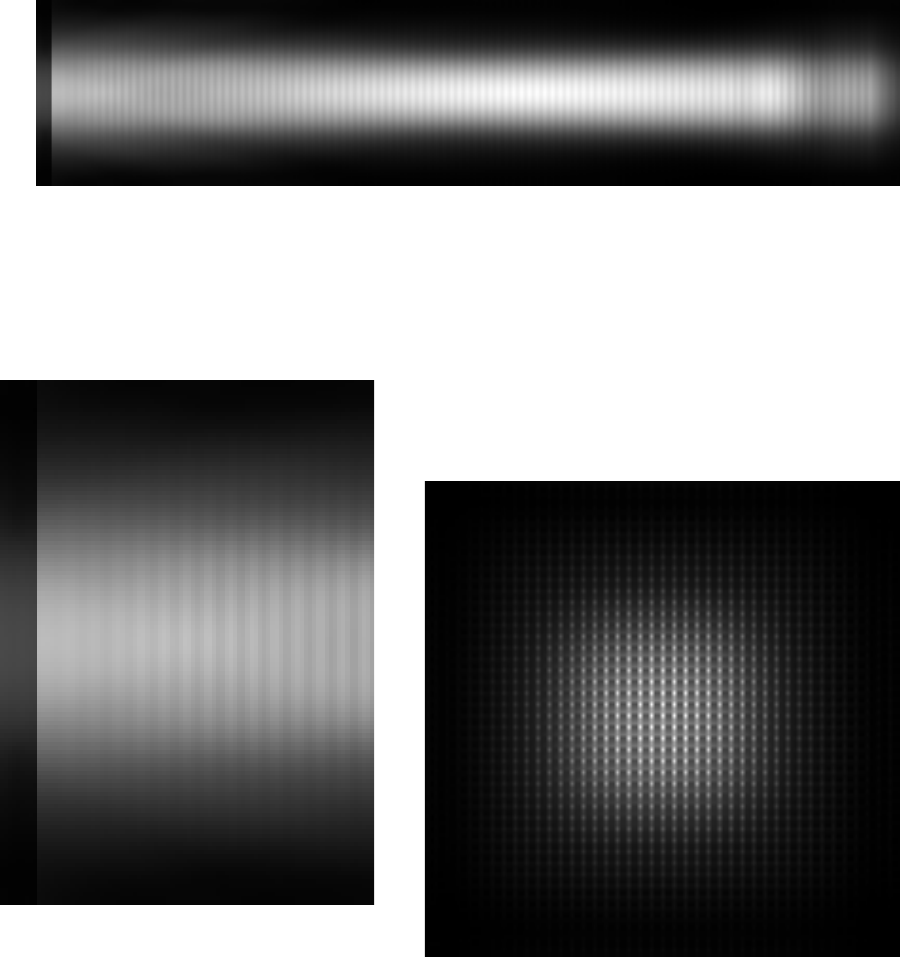
Figure 2.6 Detail of the launch end.
Note the unidirectional character of
the Gaussian beam source, and the
weak reflected field leaking back
through the illumination plane after
travelling about 110 µm.
Figure 2.7: Mode source for a 5-µm doped-silica
waveguide (∆n=0.02). This slice is taken at the
plane of the sources, showing the strong
nonuniformity.
35