DMTH4
LECTROSONICS, INC.8
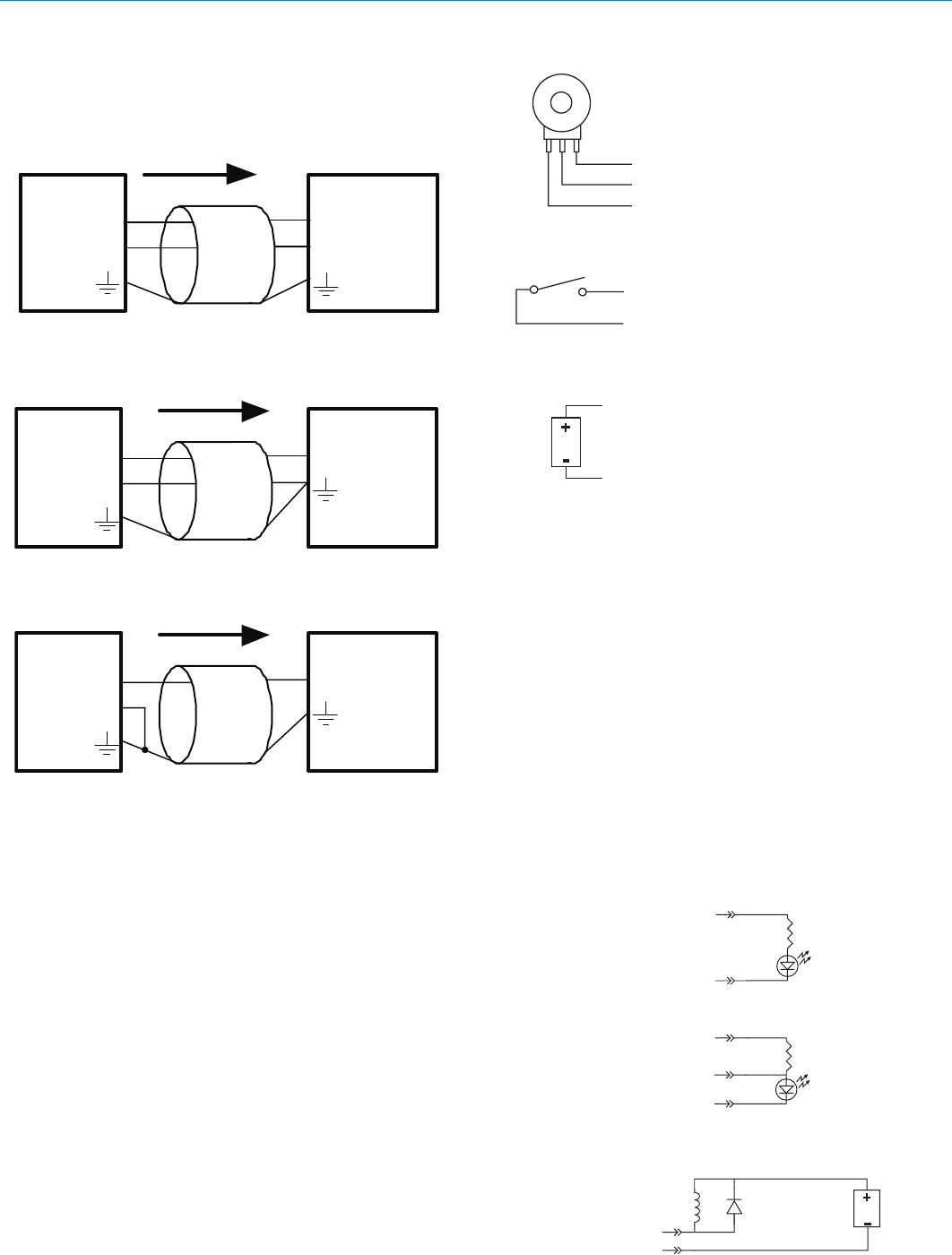
LED is on when the programmable output is active
380 Ohms
Programmable Output Pin
380 Ohms
LED is off when the programmable output is active
Programmable Output Pin
Gnd (from Programmable I/O
Pins 1, 8, 13)
1N4001
or equiv.
External
DC Voltage
Source
(<40VDC)
Relay Coil
Coil current <100mA
Programmable Output Pin
Gnd (from Programmable I/O
Pins 1, 8, 13)
Relay is on when the programmable output is active
+5VDC (from Programmable I/O
Pins 14, 20, 25)
+5VDC (from Programmable I/O
Pins 14, 20, 25)
10K Linear Potentiometer
CCW
CW
+5V
To Programmable Input Pin
Gnd
Contact Closure as Programmable Input
To Programmable Input Pin
Gnd
DC Voltage Source as Programmable Input
To Programmable Input Pin
0VDC (Off) to +5VDC (On)
Gnd
Potentiometer Connection for
Analog Control of Gain
Output RP Gain Control
on the Programmable
Inputs control tab in the Control Panel GUI. See the
Rear Panel Ctrl tab in the Control Panel software Help
for setting all programmable input parameters.
Programmable Outputs
Programmable outputs are used to indicate the current
state of a programmable input, monitor activity on
telephone or codec interfaces, and monitor active
preset changes. Each programmable output is the
electrical equivalent of a contact closure to ground.
When a programmable output is “active”, it conducts
current to ground. When the programmable output is
“inactive”, no current flows to ground. The maximum
usable voltage for the programmable outputs is 40 V
and they will safely conduct up to 100 mA DC continu-
ous. Following are some typical uses for the program-
mable outputs.
Audio Outputs (AUX and CODEC)
The AUX and Codec outputs are a balanced differential
configuration and include an attenuator to reduce the
signal to mic level. Wire these outputs as indicated in
the following illustration.
Telephone Line Jack
Connect a standard telephone cable with RJ11 connec-
tors between the back panel Telephone Line Jack and
the host telephone system.
Programmable Inputs
Programmable inputs are provided to enable external
control over a variety of parameters. Each input can
respond to a contact closure, a DC voltage source, or
the variable voltage output from a potentiometer. The
following illustrates common connections to the pro-
grammable input pins. (See also Programmable
Inputs and Outputs Wiring Example.)
No external pull-up resistors are necessary because
each programmable input is internally pulled up through
a 100K resistor to +5V. When using a continuous
voltage with one of the programmable inputs, the
function of the programmable input must be set to
either
Analog Input RP Gain Control
or
Analog
DM Out
+
-
Destination
+
-
DM Out to Balanced Input
(3-Wire)
Shield
DM Out
+
-
Destination
+
DM Out to Unbalanced Input
(3-Wire)
Shield
DM Out
+
-
Destination
+
DM Out to Unbalanced Input
(2-Wire)
Shield