7 (26)
Wireless Mark-up Language (WML) - a lightweight presentation language, similar to HyperText Mark-
up Language (HTML) but optimized for use with mobile terminals.
Wireless Mark-up Language Script (WMLS) - a lightweight script language, similar to Java Script
TM
.
Wireless Telephony Application / Interface (WTA / WTAI) - telephony services and programming
interfaces.
Content Formats - defined data formats, such as vCard and vCalendar.
2.2.3 Wireless Session Protocol (WSP)
The Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) provides the application layer of WAP with an interface for two
session services. The first is a connection-oriented service that operates above the transaction layer
protocol. The second is a connectionless service that operates above a secure or non-secure datagram
service.
The WSP is optimized for low bandwidth bearer networks with long latency.
2.2.4 Wireless Transport Protocol (WTP)
The Wireless Transport Protocol (WTP) runs on top of the datagram service and provides a lightweight
transaction-oriented protocol suitable for use in mobile terminals. WTP operates over secure or non-
secure wireless datagram networks
.
2.2.5 Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS)
The Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) is based on the industry standard Transport Layer Security
(TLS) and is optimized for used over narrow band communication channels. WTLS may be used for
secure communication between terminals, and applications can selectively enable WTLS features.
2.3 Developing Applications with WAP
Application Developers can use the principles of WAP to develop new services or adapt existing
Internet applications for use with mobile terminals. Applications are written in the Wireless Mark-up
Language (WML) and the WMLScript, and stored on either a normal web server (origin server) or
directly on the WAP Gateway. The content stored on the web server will be accessible from the mobile
terminals via the cellular network and a WAP gateway or proxy.
The Proxy Server acts as a gateway between the cellular network and the Inter/Intranet. The data sent
between the origin server and the handset is binary encoded to optimize transmission over the narrow
bandwidth of the cellular network. Note that the content stored on the web server might be in either
textual or binary format. When the WAP gateway fetches textual content, it automatically compiles
this to the encoded format to minimize network load.
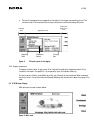
Figure 2 shows the network-related elements required for developing and offering services to mobile
users.
Wireless
Network
WAP
Proxy
WTA
Server
Binary WML
Binary
WML
HTML
Filter
WML
WML
HTML
Web
Server