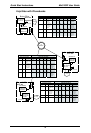
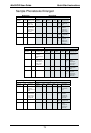
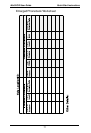
Quick Start Instructions MultiVOIP User Guide
70
Phonebook Tips
Preparing the phonebook for your voip system is a complex task that, at
first, seems quite daunting. These tips may make the task easier.
1.
Use Dialing Patterns, Not Complete Phone Numbers. You will not
generally enter complete phone numbers in the voip phonebook.
Instead, you’ll enter “destination patterns” that involve area codes and
other digits. If the destination pattern is a whole area code, you’ll be
assigning all calls to that area code to go to a particular voip that has a
unique IP address. If your destination pattern includes an area code
plus a particular local phone exchange number, then the scope of calls
sent through your voip system will be narrowed (only calls within that
local exchange will be handled by the designated voip, not all calls in
that whole area code). In general, when there are fewer digits in your
destination pattern, you are asking the voip to handle calls to more
destinations.
2.
The Four Types of Phonebook Digits Used. Important!
“Destination patterns” to be entered in your phonebook will generally
consist of:
(a) calling area codes,
(b) access codes,
(c) local exchange numbers, and
(d) specialized codes.
Although voip phonebook entries may look confusing at first, it’s
useful to remember that all the digits in any phonebook entry must be
of one of these four types.
(a)
calling area codes. There are different names for these around the
world: “area codes,” “city codes,” “country codes,” etc. These codes,
are used when making non-local calls. They always precede the phone
number that would be dialed when making a local call.