Dialogic
®
Global Call IP Technology Guide — November 2007 61
Dialogic Corporation
IP Call Scenarios
3.2.4 Unsuccessful H.450.2 Blind Call Transfer Scenarios
There are a several of scenarios where a blind call transfer may fail. The most common scenarios
are described in the following topics:
• Party B Rejects Transfer
• No Response From Party B
• No Response From Party C
• Party B Clears Primary Call Before Transfer is Completed
• Party C is Busy When Transfer Attempted
For simplification purposes, none of the following figures indicate the opening and closing of
logical channels (and the associated media sessions) because the control procedures are consistent
with typical non-transfer related H.323 calls.
3.2.4.1 Party B Rejects Transfer
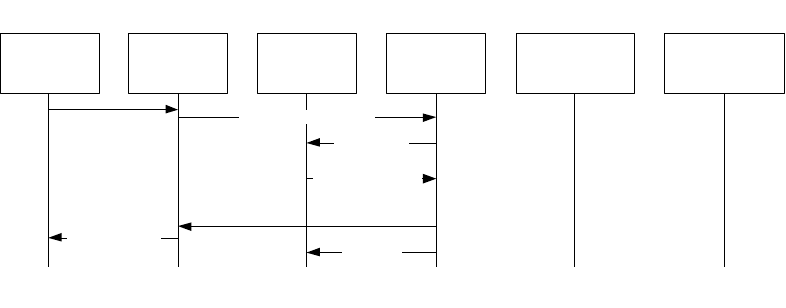
As indicated in Figure 15, the application at the transferred endpoint (party B) may call the
gc_RejectXfer( ) function to signal via the ctInitiate.ReturnResult APDU that it cannot participate
in a transfer. As a result, the GCEV_INVOKE_XFER_REJ termination event is received at
transferring endpoint (party A) and the original primary call is left connected and in the
GCST_CONNECTED state from the perspective of both A and B.
Figure 15. H.450.2 Blind Call Transfer Failure - Party B Rejects Call Transfer
A
(Transferring)
IP CCLib
B
(Transferred)
App
B
(Transferred)
IP CCLib
C
(Transferred To)
App
C
(Transferred To)
IP CCLib
gc_InvokeXfer(CRNp)
FACILITY(ctInitiate.Invoke)
Post condition: Parties A and B remain connected.
GCEV_REQ_XFER
(CRNp)
gc_RejectXfer(CRNp,
GCVAL_REJREASON_
UNAVAIL)
GCEV_
REJ_XFER
(CRNp)
Pre condition: Primary call between A and B is connected (not shown).
FACILITY(ctInitiate.ReturnResult = notAvailable)
GCEV_
INVOKE_XFER_REJ
(CRNp, GCRV_
REMOTEREJ_
UNAVAIL)
A
(Transferring)
App