35-2
Chapter 35 Configuring iSCSI
About iSCSI
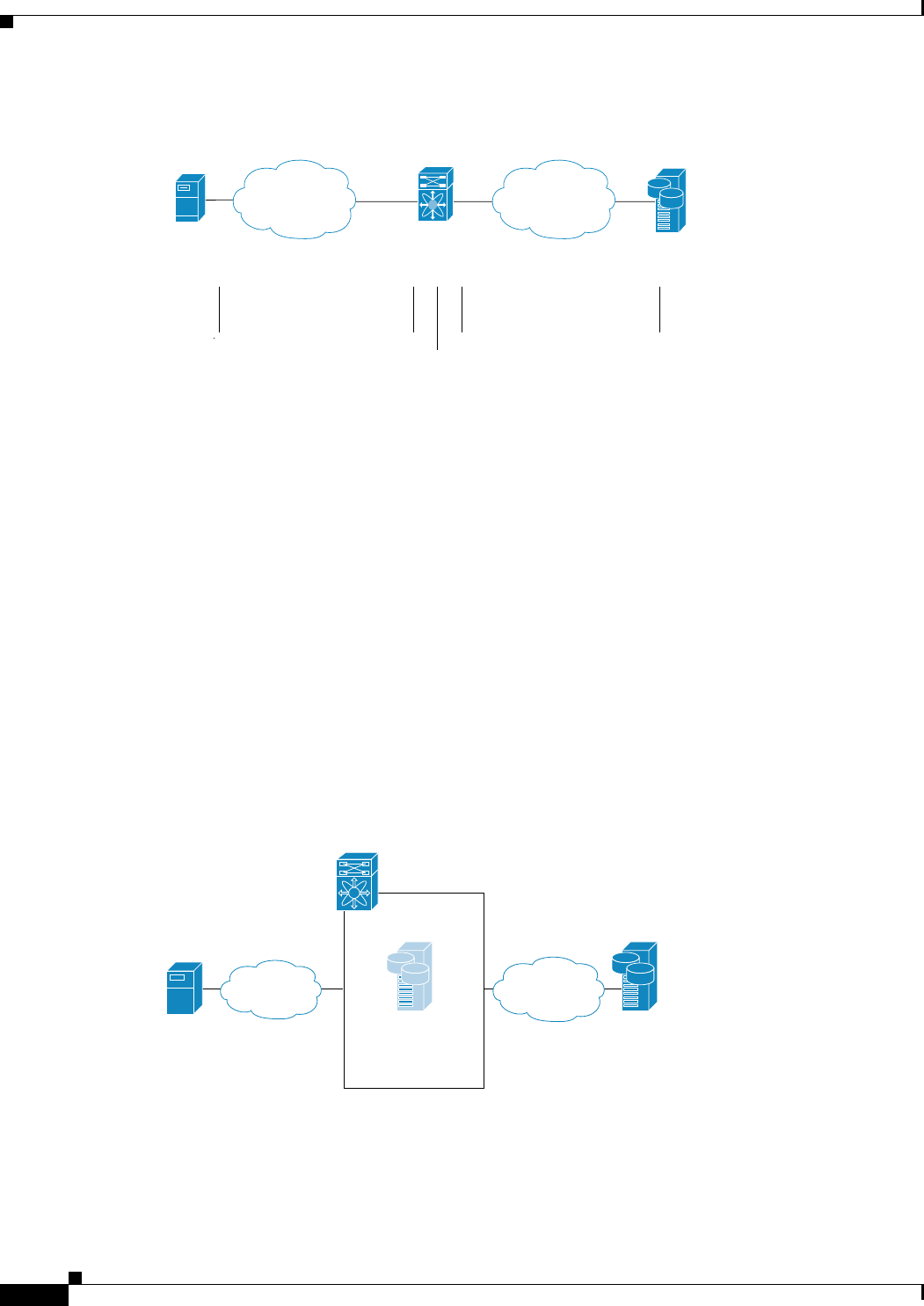
Figure 35-1 Transporting iSCSI Requests and Responses for Transparent iSCSI Routing
Each iSCSI host that requires access to storage through the IPS module or MPS-14/2 module needs to
have a compatible iSCSI driver installed. (The Cisco.com website at
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/sn5420-scsi provides a list of compatible drivers). Using the
iSCSI protocol, the iSCSI driver allows an iSCSI host to transport SCSI requests and responses over an
IP network. From the host operating system perspective, the iSCSI driver appears to be a SCSI transport
driver similar to a Fibre Channel driver in the host.
The IPS module or MPS-14/2 module provides transparent SCSI routing. IP hosts using the iSCSI
protocol can transparently access targets on the Fibre Channel network. Figure 35-1 provides an example
of a typical configuration of iSCSI hosts connected to an IPS module or MPS-14/2 module via the IP
network access Fibre Channel storage on the Fibre Channel SAN.
The IPS module or MPS-14/2 module create a separate iSCSI SAN view and Fibre Channel SAN view.
For the iSCSI SAN view, the IPS module or MPS-14/2 module create iSCSI virtual targets and then maps
them to physical Fibre Channel targets available in the Fibre Channel SAN. They present the Fibre
Channel targets to IP hosts as if the physical iSCSI targets were attached to the IP network (see
Figure 35-2).
Figure 35-2 iSCSI SAN View—iSCSI virtual targets
Switch 1
Transporting iSCSI requests
and responses over an IP
network
IP
network
Fibre
Channel
SAN
IP host A
Intelligent
storage array
AC
B
Routing SCSI requests
and responses
(Through the IPS module)
Transporting FCP requests
and responses between a Cisco
MDS switch and a storage array
91567
iscsi
iSCSIiSCSI
MDS
120871
IP
Network
Virtual iSCSI
Target T-3
Target T-3
Fibre
Channel
SAN