Configure IP Networks for Real-Time Voice Traffic
VC-20
Voice, Video, and Home Applications Configuration Guide
For more information about Multilink PPP, refer to the “Configuring Media-Independent PPP and
Multilink PPP” chapter in the Dial Solutions Configuration Guide.
Multilink PPP Configuration Example
The following example defines a virtual interface template that enables Multilink PPP with
interleaving and a maximum real-time traffic delay of 20 milliseconds, and then applies that virtual
template to the Multilink PPP bundle:
interface virtual-template 1
ppp multilink
encapsulated ppp
ppp multilink interleave
ppp multilink fragment-delay 20
ip rtp reserve 16384 100 64
multilink virtual-template 1
Configure RTP Header Compression
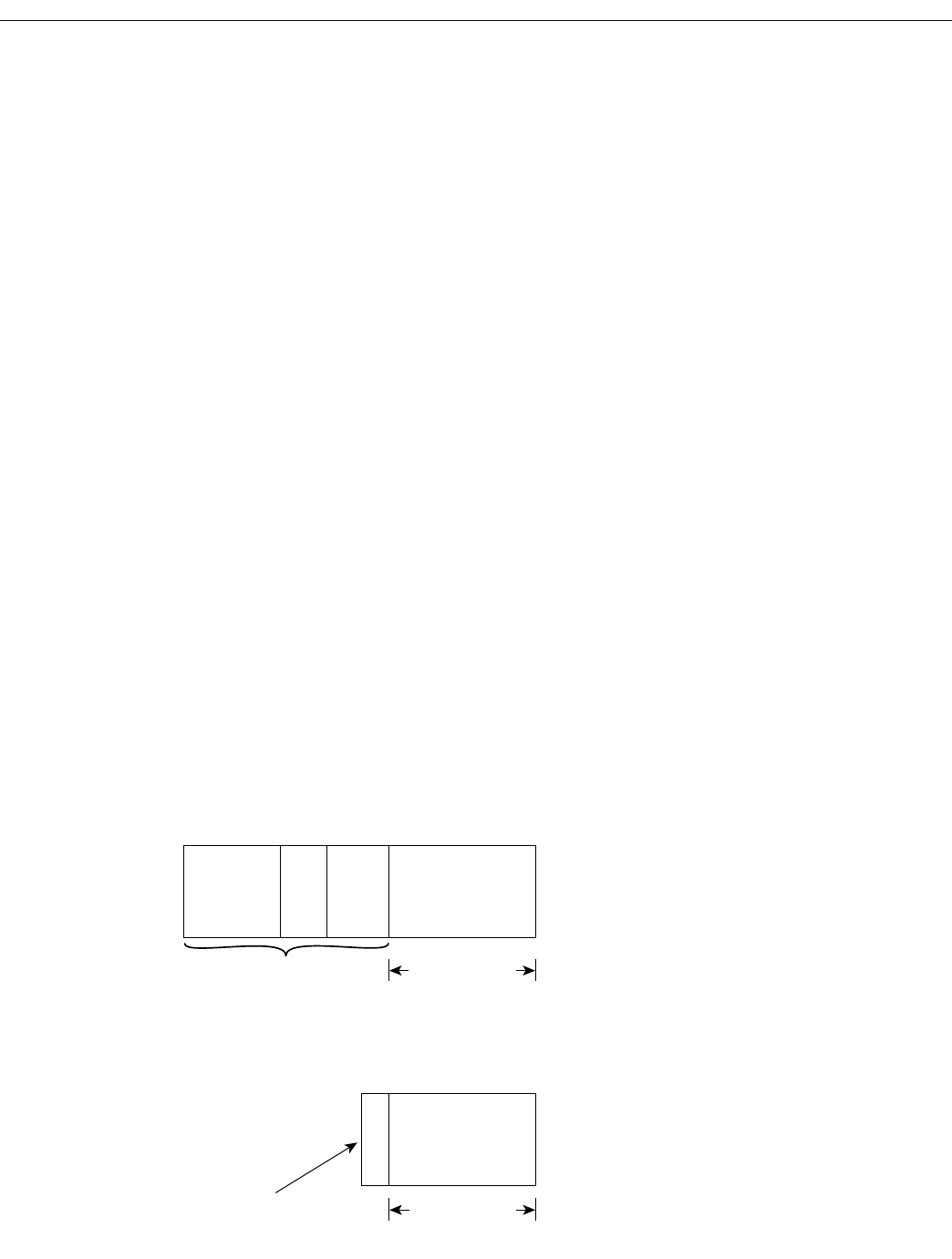
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) is used for carrying packetized audio traffic over an IP network.
RTP header compression compresses the IP/UDP/RTP header in an RTP data packet from 40 bytes
to approximately 2 to 4 bytes (most of the time), as shown in Figure 4.
This compression feature is beneficial if you are running Voice over IP over slow links. Enabling
compression on both ends of a low-bandwidth serial link can greatly reduce the network overhead if
there is a lot of RTP traffic on that slow link.
Typically, an RTP packet has a payload of approximately 20 to 160 bytes for audio applications that
use compressed payloads. RTP header compression is especially beneficial when the RTP payload
size is small (for example, compressed audio payloads between 20 and 50 bytes).
Figure 4 RTP Header Compression
Before RTP header compression:
20 bytes 8 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
12 bytes
IP
Header
UDP
RTP Payload
After RTP header compression:
2 to 4 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
IP/UDP/RTP header
Payload
12076


















